new posts in all blogs
Viewing: Blog Posts Tagged with: tax, Most Recent at Top [Help]
Results 1 - 10 of 10
How to use this Page
You are viewing the most recent posts tagged with the words: tax in the JacketFlap blog reader. What is a tag? Think of a tag as a keyword or category label. Tags can both help you find posts on JacketFlap.com as well as provide an easy way for you to "remember" and classify posts for later recall. Try adding a tag yourself by clicking "Add a tag" below a post's header. Scroll down through the list of Recent Posts in the left column and click on a post title that sounds interesting. You can view all posts from a specific blog by clicking the Blog name in the right column, or you can click a 'More Posts from this Blog' link in any individual post.

By: DanP,
on 3/4/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Finance,
tax,
economy,
banks,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Business & Economics,
Economic Policy with Richard S. Grossman,
economic policy,
american economy,
interest rates,
company tax,
Ricahrd S Grossman,
Books,
Economics,
business,
money,
Add a tag
The industrialized world is currently moving through a period of ultra-low interest rates. The main benchmark interest rates of central banks in the United States, the United Kingdom, Japan, and the euro-zone are all 0.50% or less. The US rate has been near zero since December 2008; the Japanese rate has been at or below 0.50% since 1995. Then there are the central banks that have gone negative: the benchmark rates in Denmark, Sweden, and Switzerland are all below zero. Other short-term interest rates are similarly at rock-bottom levels, or below.
The post Are ultra-low interest rates dangerous? appeared first on OUPblog.
By: Mark Myers,
on 4/15/2014
Blog:
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
family,
humor,
Men,
Government,
taxes,
Dad,
tax,
daughters,
April 15th,
Don't Blog Angry,
Add a tag
I think April 15th would be the worst birthday to have. There are two kinds of people as it relates to taxes – those who get a check and those who have to send a check. If you have to send a check (like me), you grudgingly hold onto it until the last minute and mail it on April 14th, leaving you broke and unable to buy a present for your friend with a birthday the following day. If you get a check, you filed in early February. Since you considered the return a sudden windfall, you blew it on something frivolous like a snowcone maker, leaving you no residual to buy a present for your friend with the worst birthday of the year.
Conversely, there would be something extremely cool about being a leap baby and having February 29th as your birthday.
 That tidbit is irrelevant today since I just had to write a check to the United States Treasury! Oh, I understand that it costs to provide government services. I know it has to come from the citizens. I just hate filling that out on the check – and then they want me to Fed X it or pay extra for a return confirmation. I’m sorry, but aren’t I paying for the postal service to be sufficient to deliver your money to you? If you have any doubts whether the man in blue who just took my envelop can discharge his duty properly, shouldn’t you institute a better employee screening process instead of charging me another $4.50?
That tidbit is irrelevant today since I just had to write a check to the United States Treasury! Oh, I understand that it costs to provide government services. I know it has to come from the citizens. I just hate filling that out on the check – and then they want me to Fed X it or pay extra for a return confirmation. I’m sorry, but aren’t I paying for the postal service to be sufficient to deliver your money to you? If you have any doubts whether the man in blue who just took my envelop can discharge his duty properly, shouldn’t you institute a better employee screening process instead of charging me another $4.50?
I’m not bitter, though. Not at all.
But while I’m on the subject, I remember when I took my first baby home from the hospital in mid-December. When I did my taxes, I felt like I had cheated the world since I got a deduction for the entire year and she only cost me for two weeks. That was eighteen years ago. So this year I lost the tax credit for her because she turned eighteen. I love her dearly, but like most children, she is complete financial dead weight – all cost, little contribution. And let me tell you Mr. United States Treasury, she costs considerably more now at eighteen than she did at one. I’d trade diapers and formula for cell phones, clothes, gas and car insurance any day.
I’m not bitter, though. Not at all.
I could go on, about paying into a social security system that I am assured will not exist when I am of age to need it. That’s why I had four kids, they are a kind of a retirement plan for me. I figure I can rotate a week a month at each of their houses and mooch off them just to pay them back. I’ll refuse to wear pants, make odd noises and smells, and sit on the front porch complaining about the government all day.
I’m not bitter, though. Not at all…

♦
Photo credit: Robert N. Dennis Collection of Stereoscopic Views
Artwork: The Taxes by Orlov



By: Kirsty,
on 11/14/2011
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
tax,
Thought Leaders,
labour,
housework,
single women,
*Featured,
Business & Economics,
labour market,
allocation,
alexander gelber,
earned income tax credit,
labour policy,
review of economic studies,
single men,
tax allowances,
gelber,
“quality,
busier,
work,
Economics,
wharton,
policymakers,
business,
Current Affairs,
Add a tag
By Alexander M. Gelber
When tax incentives draw single women into the labour force, what activities do they sacrifice? Do they spend less time enjoying leisure? Do they cut back on household chores? Do they give up time with their children?
Over the past thirty years, US policymakers tried to increase participation of single mothers in the labour force by expanding the Earned Income Tax Credit and reforming the welfare system. One key motivation for reform was the perception that some single mothers were choosing to be idle and instead ought to contribute more productively to society by working. But did the policy reforms induce single mothers to shift from one productive activity – work at home – to another – work in the market? In a new paper published in the Review of Economic Studies, we find that the answer is “yes”: tax policy largely shifts single women between work at home and work in the market. Interestingly, however, when tax incentives draw them into the labour force, they may not cut much from their “quality time” with their children.
Remarkable patterns in the data suggest that tax policy had a very important effect on the labour supply and housework decisions of single women over this period. From the mid-1980s to the mid-to-late-1990s, the incentive to participate in the labour force greatly increased for single women with children relative to those without children. This was largely due to major expansions of the Earned Income Tax Credit—which transfers money to low-income single households only if they participate in the labor force—and cutbacks in welfare, both of which impacted low-income single women.
The figure below shows that over the same period of years, hours of market work for single women with children increased substantially relative to those without children, as previous literature has documented. This suggests that the changes in policy may have been responsible for the large changes in market work over the same period.
Strikingly, the pattern for housework looks like a mirror image of the pattern for market work. Hours of housework fell substantially for women with children relative to those without children over the period of the primary policy changes, with little relative change outside of this period. The relative fall in housework accounts for over half of the relative increase in market work, suggesting that most of the change in market work came out of housework. We find that for every additional hour that a single woman spends working in the market in response to a change in tax policy, she spends about 40 minutes less time working at home.
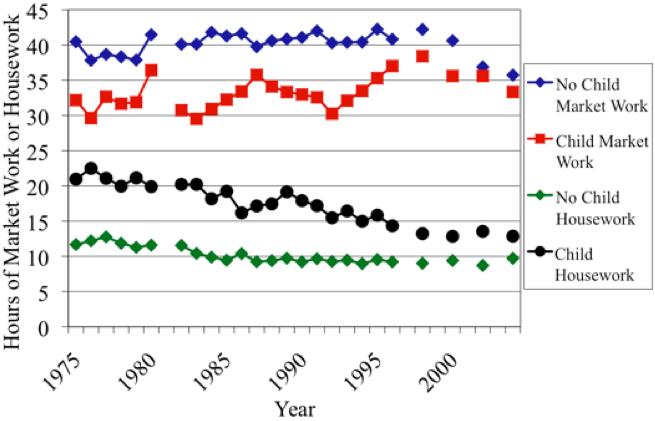
Mean usual hours of market work and housework of single women with and without children, 1975-2004
Importantly, we find no evidence that single women’s amount of time spent with children (as the primary activity, i.e. “quality time”) decreases significantly. We also find that single women’s time spent eating and preparing food decreases and that time spent sleeping changes insignificantly.
We find evidence that single women’s purchases of food away from home, such as takeout and restaurant meals, increase in response to an increase in the incentive to participate in the labour force. This makes sense: Women are busier when they enter the labour force and make up some of the time by purchasing food prepared by others instead of themselves. We also find some evidence that overall food purchases rise. Single women thus appear to use market goods to substitute for time: they become busier when they enter the labor force and save time by buying food in the market instead of themselves spending time on food.
Interestingly, howev

By: Rebecca,
on 5/3/2010
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Obama,
tax,
Edward Zelinsky,
goverment,
deficit,
VAT,
Economics,
Law,
Politics,
Current Events,
A-Featured,
Finance,
debt,
Add a tag

By Edward Zelinsky
A federal value-added tax (VAT) is today’s magic bullet for slaying the federal budget deficit. A federal VAT would be a veritable cash cow, obviating the need for painful measures like serious spending reductions and middle class income tax hikes. A VAT would be more regressive and complex than its proponents acknowledge. Like most putative panaceas, a VAT should be rejected.
VATs are national sales taxes, widely used in Europe. Unlike a conventional retail sales tax, a VAT requires that, at each stage of production, manufacturers add to the cost of goods (and services) a tax reflecting the value added at that stage. The cumulative VAT payments paid as a product is made become part of the final price paid by the purchaser when he buys the finished product.
Among the influential proponents of a VAT is former Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker. Some observers assert that President Obama’s National Commission on Fiscal Responsibility and Reform is designed to provide Mr. Obama with the political cover to propose a VAT after this year’s mid-term elections. This perception was reinforced by Mr. Obama when he said he is open to all budgetary “options,” including a VAT. Among the other prominent passengers on the VAT bandwagon is former President Bill Clinton.
Many who advocate a VAT are sincerely concerned about federal deficits and believe that tax increases in the form of a federal VAT must be the solution. However, the case for a federal VAT is unconvincing.
We don’t need another layer of taxation in our federal tax system. However, a VAT, placed on top of existing federal taxes, would be just that, adding to the complexity and regressivity of the federal tax system.
Some VAT proponents tout it as a means of simplifying the federal tax system. A portion of VAT revenues, they argue, can be used to remove more, perhaps most, Americans from the burden of paying the federal income tax.
These claims should be met with skepticism. Even if a portion of VAT revenues are initially used to relieve some taxpayers’ federal income liabilities, for the long term, a VAT would likely be added on top of federal income taxes for individuals and corporations.
Taxes should be transparent, making clear to voters the price of government so that they can assess the benefits of public activities against such activities’ costs. A VAT, in contrast, is largely hidden since it is embedded in the prices of the goods and services consumers buy.
VAT proponents retort that, when a customer purchases a product or service, the amount of tax built into the price will be disclosed. It is, however, unlikely that such disclosure will in practice prove meaningful.
While VATs made sense in the European context after World War II, the European model of public finance looks less attractive today with Greece, Portugal and Spain teetering on the edge of national bankruptcy.
Moreover, a VAT would fit uncomfortably into the existing structure of U.S. public finance. A national VAT would compete with and eventually crowd out the retail sales taxes which are central to the fiscal autonomy of the states. We value the financial independence of the states in a way that Europeans do not prize the autonomy of their provinces.
VAT proponents contend that a VAT, as a tax on consumption, will incent Americans to save more by increasing the cost of consumption. However, most federal taxpayers are already encouraged to save on a tax-advantaged

By: Rebecca,
on 1/4/2010
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Economics,
Law,
Business,
Politics,
shopping,
holiday,
A-Featured,
online,
tax,
economy,
Edward Zelinsky,
Amazon laws,
internet sales,
Add a tag

By Edward Zelinsky
As a critical element of the holiday shopping season of 2009, internet sales have matured into a pivotal part of the American economy. The modest, but important, increase in 2009 holiday sales over the 2008 shopping season is largely attributable to increased online purchases.
This emergence of internet sales highlights an important problem of public finance which, so far, Congress has been unwilling to address: Most internet purchases are effectively sales tax-free even as equivalent purchases at traditional brick-and-mortar stores are taxable. The resulting discrepancy is neither fair nor efficient as conventional merchants, required to collect sales tax from their customers, find themselves unfairly competing with internet sellers who do not.
The legal cause of this discrepancy is the decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in Quill Corporation v. North Dakota. In that case, the Court held that a state, on its own, can only impose sales tax collection responsibilities on a seller with a physical presence in that state. However, Congress, the Quill Court stated, can require out-of-state sellers to collect state sales taxes from their mail order and internet customers. So far, Congress has been unwilling to impose this general sales tax collection responsibility on internet sellers.
As a matter of law, if sales tax is not collected by an internet (or mail order) seller, the customer must himself pay tax on his purchases to the state in which he lives. In practice, the states can rarely enforce this legal obligation to pay sales tax since the states must rely on customers to self-report their internet purchases. Unsurprisingly, compliance with this taxpaying obligation is not high.
The upshot is an unacceptable situation in which firms with physical facilities in a particular state must collect sales taxes from their customers in that state while the burgeoning internet retail sector sells the same and equivalent goods sales effectively tax-free.
Given the dependence of most state governments on sales tax revenue, the de facto tax-free nature of most internet sales is an enormous problem for state budgets, already reeling from the economic effects of the Great Recession. Now it turns out that the modest resurgence of consumer sales in 2009 and, with luck, in 2010 will not produce an equivalent recovery of state sales tax revenues since much of that resurgence is attributable to internet sales on which the states effectively collect little or no sales tax.
The states have been aware of this problem for some time and have been lobbying Congress for federal legislation to require internet and mail order sellers to collect state sales taxes from their customers. As yet, however, Congress has not responded to these entreaties. Recently, several states, in particular New York, Rhode Island and North Carolina, unilaterally enacted so-called “Amazon Laws,” designed to force internet retailers (of which Amazom.com is most prominent) to collect sales taxes by virtue of such retailers’ “associates programs” in those states. However, the efficacy of these laws is doubtful, not least because Amazon.com and other internet sellers can respond to such laws by terminating their associates programs in the states adopting these sales tax collection laws.
Moreover, the fiscal straits of the states are likely to get worse as the Congress and the Obama administration appear determined, as part of federal health care legislation, to impose upon the states new unfunded mandates in the form of expanded Medicaid outlays.
All of these factors

By: Rebecca,
on 5/4/2009
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Business,
Politics,
A-Featured,
Law,
new york,
tax,
workplace,
telecommute,
interstate,
swine flue,
Add a tag

By Edward Zelinsky
The swine flu is back. Gerald Ford was president the last time Americans confronted the swine flu. In response to the current emergence of this disease, public health authorities advise us to take precautions including the avoidance of crowds and of unnecessary travel. For many Americans, the most significant exposure to the danger of communicable disease occurs at the workplace.
While this workplace-based exposure cannot be eliminated, it can be minimized. To combat swine flu, we should encourage employees to telecommute from their homes rather than travel to their employers’ offices with their attendant danger of communicable disease.
Modern technologies – the internet, email, cell phones, electronic data bases – enable many employees to work from their homes for at least part of the week. Telecommuting extends job opportunities to individuals for whom traditional commuting is difficult, for example, the disabled, parents of small children, persons who live far from major employment centers. Telecommuting is also good for the environment, reducing the carbon footprints of employees who spend some of their work days at home and need not physically commute to work on those days.
Now, telecommuting can achieve yet another important benefit by reducing individuals’ potential exposure to swine flu on the days they work at home rather than travel to their employers’ offices.
A major impediment to telecommuting is New York State’s extraterritorial taxation of nonresidents’ incomes. When a nonresident works at home for a New York employer, New York imposes income tax on the telecommuting nonresident for this out-of-state day even though the nonresident never sets foot in New York on that day and even though New York provides no public services to the nonresident telecommuter on his day working at his out-of-state home. The result of New York’s extraterritorial taxation is typically double income taxation of the nonresident for telecommuting from outside the Empire State, a classic confirmation that no good deed goes unpunished.
I am something of a poster boy for the irrationality of New York’s extraterritorial taxation of nonresident telecommuters. I am a law professor in Manhattan at the Benjamin N. Cardozo School of Law of Yeshiva University. I live in New Haven, Connecticut. When New York sought to impose its income tax on me for the days I wrote and researched at home in Connecticut, I challenged this extraterritorial tax on constitutional grounds. Virtually all independent legal commentators concluded that this challenge should have prevailed since the Due Process and Commerce Clauses of the U.S. Constitution prevent the states from taxing activity which occurs outside their respective borders.
Nevertheless, despite these constitutional principles, New York’s courts held that New York can tax me (and other telecommuters) on days worked at home outside the Empire State. New York’s Court of Appeals, that state’s highest court, specifically approved New York’s tax-based discouragement of nonresidents’ telecommuting from their out-of-state homes.
Enter the swine flu.
For the duration of swine flu problem, New York should encourage telecommuting or at least not impede it. In particular, New York Governor David Paterson should announce that, to stimulate telecommuting to combat potential exposure to the new swine flu, New York will suspend its extraterritorial income taxation of nonresidents for all days such nonresidents work at their out-of-state homes.
In any event, Congress should pass the Telecommuter Tax Fairness Act which, if enacted into law, would prevent states from taxing telecommuting nonresidents on the days they work at their out-of-state homes.
And who knows? After the swine flu danger is over, Governor Paterson and New York’s other policymakers may discover the long-term benefits to New York of reforming permanently New York’s extraterritorial (and unconstitutional) taxation of telecommuters like me.
Edward A. Zelinsky 
is the Morris and Annie Trachman Professor of Law at the
Benjamin N. Cardozo School of Law of Yeshiva University. He is the author of
The Origins of the Ownership Society: How The Defined Contribution Paradigm Changed America.


By: Rebecca,
on 2/9/2009
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Economics,
Law,
Politics,
A-Featured,
old,
new,
tax,
wealth,
Zelinsky,
grandfather,
grandfather exemption,
GST,
new wealth,
old wealth,
exemption,
Add a tag

By Edward Zelinsky
In light of the Democratic party’s control of both houses of Congress and the White House, it is probable that the federal government will continue to levy an estate tax when affluent decedents transmit their wealth to their descendants. The most likely possibility is that Congress will continue to exempt decedents’ estates valued less than $3.5 million while it taxes estates exceeding that threshold amount. In light of President Obama’s statements on the subject, it is also probable that such excess will taxed at a 45% rate when a decedent dies and leaves his wealth to his descendants.
Important details remain to be determined, e.g., whether the $3.5 million federal estate tax exemption will be adjusted annually for increases in the cost of living; whether various estate tax planning techniques such as family partnerships will be curbed or eliminated.
How ever these matters are ultimately resolved, the legislation perpetuating the federal estate tax should contain a provision subjecting to federal taxation all large intergenerational transfers of family wealth. Specifically, Congress should repeal the grandfather exemption from the federal generation skipping tax (GST) for irrevocable trusts established on or before September 25, 1985. This exemption unfairly immunizes from federal taxation transfers at death of “old” wealth while economically equivalent transfers of new wealth are taxed.
As an historic matter, the federal estate tax was often avoided through the use of so-called generation skipping trusts. When a decedent established such a trust, the trust continued for his children, grandchildren and great-grandchildren with no further federal estate taxation being due whenever any of these lineal descendants themselves subsequently died.
The term “generation skipping trust” was a misnomer. The trust didn’t skip any generations. The tax did. Families could continue to enjoy and grow inherited wealth in trust without paying federal estate taxes.
In 1986, Congress prospectively outlawed this planning technique by imposing the federal GST. The GST backstops the federal estate tax by assessing a tax on a death-related transfer of wealth in trust whenever an equivalent transfer outside of a trust would trigger the estate tax. Thus, with the GST in place, families can no longer use trusts to avoid taxation on intergenerational transmissions of large fortunes. Rather, federal taxation must be paid at least once in every generation.
However, Congress grandfathered from the GST transfers of wealth from trusts which were in existence and irrevocable on September 25, 1985.
This exemption creates for federal tax purposes an unfair and unconvincing distinction between new wealth (think Michael Bloomberg) and old wealth (think the Kennedys and the Rockefellers). Because of the federal GST, families inheriting new wealth now pay a federal estate tax or its equivalent at least once every generation. However, families inheriting old wealth live estate-tax free by virtue of the grandfathered status of tax-avoiding trusts established by such families’ patriarchs and matriarchs on or before September 25, 1985.
There are respectable arguments for and against federal estate taxation. However, if there is to be an estate tax, there is no convincing reason to treat differently old wealth from new wealth.
If, as the President Obama and the current Congress apparently believe, federal estate taxation represents sound social and tax policy, there is no warrant for continuing to exempt from such taxation some families simply because they had the good luck to make their fortunes before 1985. As part of its legislation continuing the federal estate tax, Congress and the President should eliminate the immunity from generation skipping taxation for intergenerational wealth transfers accomplished by irrevocable trusts established on or before September 25, 1985. For federal tax purposes, all inherited wealth should be taxed the same, whether it is “old” wealth or “new” wealth. The GST grandfather exemption should be abolished.
 Edward A. Zelinsky
Edward A. Zelinsky is the Morris and Annie Trachman Professor of Law at the
Benjamin N. Cardozo School of Law of Yeshiva University. He is the author of
The Origins of the Ownership Society: How The Defined Contribution Paradigm Changed America.

By: Rebecca,
on 4/9/2008
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Law,
Politics,
Current Events,
A-Featured,
Hillary Clinton,
clinton,
Finance,
income,
President Clinton,
tax,
tax return,
wealth,
subsidy,
taxable,
clintons’,
taxpayers,
clinton’s,
package,
taxpayer,
return,
Add a tag
Edward A. Zelinsky is the Morris and Annie Trachman Professor of Law at the Benjamin N. Cardozo School of Law of Yeshiva University. He is the author of The Origins of the Ownership Society: How The Defined Contribution Paradigm Changed America. In the article below he looks at the Clinton’s federal tax returns.
President and Senator Clinton’s federal tax returns provide much fodder for commentators who are debating a diverse set of questions in light of those returns: Has Mr. Clinton understandably maximized his post-presidential income in our celebrity-crazed culture – or has he exploited the presidency for unseemly financial gain? Does the Clintons’ private foundation reflect a worthy model of charitable giving – or the federal fisc’s subsidization of Senator Clinton’s presidential candidacy? Was Mr. Clinton financial relationship with Yucaipa appropriate for a former president – or for the spouse of a prospective president?
The Clintons’ tax returns raise one further issue which also requires public discussion: The federal subsidy the Clintons have received over the last seven years while earning in excess of $100 million. Mr. Clinton’s aggressive pursuit of post-presidential income is incompatible with the extensive public support he has received from federal taxpayers since leaving office. That public support was designed to preclude the nation’s chief executives from facing financial hardship after their terms of office. It was not intended to subsidize the aggressive pursuit of a post-presidential fortune.
the extensive public support he has received from federal taxpayers since leaving office. That public support was designed to preclude the nation’s chief executives from facing financial hardship after their terms of office. It was not intended to subsidize the aggressive pursuit of a post-presidential fortune.
The federal taxpayer’s subsidy of Mr. Clinton has several components. First, as a former president, Mr. Clinton is entitled to receive, for the remainder of his life, the salary of a cabinet secretary. That salary is today $191,000 per annum. In addition, as a former president, Mr. Clinton also receives, at taxpayer expense, “suitable office space appropriately furnished and equipped.” Mr. Clinton’s office in New York City costs federal taxpayers over $700,000 per year to lease and operate. Federal taxpayers also defray the salary and benefits for office staff and some of Mr. Clinton’s travel outlays. The General Services Administration currently budgets for all of these costs a yearly total of $1,162,000 for Mr. Clinton. The equivalent annual figures for former President Bush and former President Carter are $786,000 and $518,000 respectively.
In addition, Mr. Clinton is also entitled, at taxpayer expense, to Secret Service protection for the remainder of his lifetime – even though, as president, Mr. Clinton signed legislation limiting Secret Service protection for his successors to the first ten years after they leave office.
For most Americans, Mr. Clinton’s package would constitute a heady lifestyle. For President and Senator Clinton, however, this post-presidential package merely provided a tax-financed base for the aggressive pursuit of unprecedented financial gain for a former chief executive.
Mr. Clinton has apparently treated as tax-free much of the federal largesse he has received. While the Clintons’ federal tax returns report as taxable income his cabinet-level salary payments, he has apparently elected to exclude from his taxable income the other benefits he receives, namely, his federally-financed office, staff, travel costs and protection.
If the Clintons had treated these items as taxable, they most likely would have been reported on their Forms 1040 on line 21 for “other income”. On the Clintons’ 1040 for 2006, line 21 is blank, suggesting that they did not include in income the office, staff, travel costs or protection provided to them by federal taxpayers.
The tax-free treatment of this federal subsidy of Mr. Clinton makes it particularly valuable for him.
This post-presidential package and the federal subsidy it represents were not intended as a conventional deferred compensation arrangement. They instead reflect the judgment that former presidents should not be required to hustle in the marketplace after they leave office.
The story of an impoverished Ulysses Grant, financially-impelled to write his memoirs as he was dying of cancer, is an iconic image of American history. From this tragedy, the world received one of the great military autobiographies of all time. However, most Americans would prefer that the nation’s former leaders not confront the kind penury which plagued Grant at the end of his life.
The immediate stimulus for the modern post-presidential compensation package was the report that former president Truman lacked the resources to return his mail from the American public.
This post-presidential package was designed to preclude Grant’s and Truman’s successors from experiencing the financial problems they confronted. It was not intended to serve as a federal subsidy for the aggressive pursuit of a post-presidential fortune.
President Clinton is not required to accept all or any of the proffered subsidy from the federal Treasury. He can also make a payment to the federal fisc reimbursing it, in whole or in part, for the costs of this subsidy. Such reimbursement could, for example, be geared to the taxes Mr. Clinton would pay if his post-presidential benefits were treated as taxable income.
The federal taxpayers provide post-presidential benefits so that former chief executives will not replicate the unfortunate financial history of Grant or even the more moderate financial discomfort in which President Truman found himself. We do not subsidize former presidents so that they may pursue lucrative private sector careers. As a federal taxpayer subsidizing Mr. Clinton’s lifestyle, I hope he feels my pain.
ShareThis

Aeschylus
"And even in our sleep pain that cannot forget falls drop by drop upon the heart, and in our own despair, against our will, comes wisdom to us by the awful grace of God."I 've teamed up with a group of bloggers on blog catalog today who are blogging to stop abuse.
Everyday we read the horrifying details of some form of abuse in the newspaper. Whether the article is about the victim or the perpetrator it's origin is always the same, the plot always familiar, and the results life altering. By blogging together in an effort to stop abuse, we're in fact saying no more abuse, no way, not on our watch!
It's horrifying to read that some
40 million children are subject to abuse this year alone, and that many of that number, will never speak of it. Their perpetrators will move on and the world will keep turning in much the same way, except in the eyes of the child involved. For them, their nightmarish existence will continue somewhere in the back of their mind, for the rest of their lives. The victim of abuse retreats into a secret silent world of introspection, often developing an inappropriate inner dialogue of distorted ideas about themselves and the world around them.
Anyone whose experienced abuse has endured an unbreathable pain, that most of us can't begin to understand.
The child abuse victims today are our future tomorrow, and will join a society of bankers, lawyers, doctors, mothers, fathers, etc...
The heartbreaking number of combined abuse statistics has the semblance of a battleground lost to a powerful enemy. That is to say, the combined statistics are emotionally disturbing, to overwhelming a concept to comprehend. Nevertheless, if we work together educating ourselves and others on what we can do as a society to prevent abuse, then we have the framework for a battle won.
When I think of the wasted years and lives of just the few people I know who have suffered from abuse it's horrifying. We must be careful not desensitize ourselves or worse yet, develop an attitude of indifference to the way we think about abuse.
Indifference, to me, is the most intolerable of emotions, the likes of which will rear its ugly head and devour us if we're not careful. What I mean is, what we're indifferent about will often come back to haunt us in the most poetic sense of the word.
When we see signs of abuse or something wrong, we must trust our instincts and do something about what we're feeling or thinking. When we accept a more popular view rather than follow our own instincts, we lose the capacity to be honest with ourselves and others. This attitude breeds tolerance for certain behaviors that at one time, we might have deemed unacceptable.
Here is the link to a post I wrote on an incident I witnessed
involving child abuse. I feel I was guilty of the very thing I'm protesting here.
Because, the event happened in a public area, I questioned my ability to judge whether it was considered abuse. Then to my astonishment I saw there wasn't anyone else reacting either to a three year old child being slapped across the face! (Not even the security guard in the waiting area.)
In addition, others in the waiting room, including the perpetrator, looked at me as if they wished to say, " Mind your own business." I felt like saying, "Forgive me, but your child is screaming and you're more worried about me staring at you!"
Well there you have it, my contribution to and public support of a social community obviously dedicated to the "power of the pen." A virtue I admire and am honored to have been a part.
Please feel free to check out the link to my post
"Spanking Where Do You Draw The Line?" and please understand this post is not against parents spanking their children. What the post is meant to suggest is the lack of this Mother's ability to draw the line, between what is spanking and what is abuse.



 That tidbit is irrelevant today since I just had to write a check to the United States Treasury! Oh, I understand that it costs to provide government services. I know it has to come from the citizens. I just hate filling that out on the check – and then they want me to Fed X it or pay extra for a return confirmation. I’m sorry, but aren’t I paying for the postal service to be sufficient to deliver your money to you? If you have any doubts whether the man in blue who just took my envelop can discharge his duty properly, shouldn’t you institute a better employee screening process instead of charging me another $4.50?
That tidbit is irrelevant today since I just had to write a check to the United States Treasury! Oh, I understand that it costs to provide government services. I know it has to come from the citizens. I just hate filling that out on the check – and then they want me to Fed X it or pay extra for a return confirmation. I’m sorry, but aren’t I paying for the postal service to be sufficient to deliver your money to you? If you have any doubts whether the man in blue who just took my envelop can discharge his duty properly, shouldn’t you institute a better employee screening process instead of charging me another $4.50?







Brilliant! Here in the UK income tax is taken from weekly/monthly income as we are paid throughout the year. 99% of the population never see/do a tax return.
We are not bitter the whole year – every year! Not at all!
Not at all! We get them taken out to, but it is never perfect and you either end up owing or getting a refund. Love that…but I’m not bitter.
We LOST$200,000 on a property sale last year so we are actually getting money back this year. Just enough to pay the tax preparer LOL!
Mark, brilliant piece. I had already “almost” forgotten the six figure check I also mailed yesterday. It doesn’t bother as much as it used to though. I guess getting older has it’s benefits. One thing that still gets to me though is the $5,000 it cost me to find out how much I owe. Ridiculous!!! Keep smiling my friend. Still praying for you and your family.
Thanks, we can not be bitter together.
Prayers appreciated! We are fighting.
Losing money on a land deal AND paying, wow…the double whammy. Sorry, don’t be bitter,
“I’ll refuse to wear pants, make odd noises and smells, and sit on the front porch complaining about the government all day.”
–Sooooo funny. I had to laugh out loud, once again.
But you’re not bitter though eh :-)
I’m not bitter at all… Not at all….
:-)
glad you are not bitter and your retirement plan sounds very similar to mine. i have told each of my 3 daughters that i will live with each of them for 4 months a year, on a rotating basis and hopefully they each live in a warm climate. they told me that they’ve discussed it and it would be worth it for everyone to just pitch in for an apartment and a friendly nurse for me. ) hmmmm……..