new posts in all blogs
Viewing: Blog Posts Tagged with: marijuana, Most Recent at Top [Help]
Results 1 - 13 of 13
How to use this Page
You are viewing the most recent posts tagged with the words: marijuana in the JacketFlap blog reader. What is a tag? Think of a tag as a keyword or category label. Tags can both help you find posts on JacketFlap.com as well as provide an easy way for you to "remember" and classify posts for later recall. Try adding a tag yourself by clicking "Add a tag" below a post's header. Scroll down through the list of Recent Posts in the left column and click on a post title that sounds interesting. You can view all posts from a specific blog by clicking the Blog name in the right column, or you can click a 'More Posts from this Blog' link in any individual post.

By: Brittany Hobson,
on 7/20/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
american law,
American political system,
drugs laws,
john dinan,
publius: the journal of federalism,
sam kamin,
Journals,
Politics,
marijuana,
Social Sciences,
medical marijuana,
*Featured,
Publius,
oxford journals,
federalism,
Add a tag
Although in the U.S. marijuana remains illegal under federal law, a number of states have legalized marijuana in some fashion. Sam Kamin, author of “The Battle of the Bulge: The Surprising Last Stand Against State Marijuana Legalization,” agreed to answer several questions from John Dinan, editor of Publius: The Journal of Federalism
, about recent developments in this area and the future of marijuana law reform in the U.S.
The post Marijuana legalization in the American states: recent developments and prospects appeared first on OUPblog.

By: Elizabeth Gorney,
on 5/7/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Books,
coffee,
brain,
Food & Drink,
marijuana,
neuroscience,
caffeine,
*Featured,
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Gary L. Wenk,
How Chemicals Control Your Thoughts and Feelings,
endogenous marijuana neurotransmitter system,
synaptic adenosine receptor,
THC,
Your Brain on Food,
Add a tag
Does coffee enhance marijuana? A study published recently in the Journal of Neuroscience (Vol 34 (19):6480-6484, 2014) by neuroscientists from the Integrative Neurobiology Section of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, a branch of the National Institutes of Health, has finally provided a definitive answer: Yes, No, and it depends.
The post The role of marijuana in your coffee addiction appeared first on OUPblog.

By: Elizabeth Gorney,
on 4/16/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
alzheimer's,
*Featured,
Science & Medicine,
Health & Medicine,
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Gary L. Wenk,
age-associated memory loss,
anandamide,
behavioral changes,
hallucinogen,
neurogenesis,
Books,
marijuana,
Add a tag
Can smoking marijuana prevent the memory loss associated with normal aging or Alzheimer’s disease? This is a question that I have been investigating for the past ten years. The concept of medical marijuana is not a new one. A Chinese pharmacy book, written about 2737 BCE, was probably the first to mention its use as a medicine for the treatment of gout, rheumatism, malaria, constipation, and (ironically) absent-mindedness.
The post Can marijuana prevent memory decline? appeared first on OUPblog.

By: Elizabeth Gorney,
on 3/29/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Your Brain on Food,
Gary L. Wenk,
How Chemicals Control your Thoughts and Feeling,
aging brain,
cocoa powder,
memory formation,
Books,
chocolate,
exercise,
diet,
Food & Drink,
marijuana,
*Featured,
Add a tag
Everyone knows that aerobic exercise is good for the body, but is it always as good for brain? Furthermore, is exercise better than eating lots of chocolate for the aging brain? A recent study published in the journal Nature Neuroscience by a group of scientists from Columbia University and NYU gave a large daily dose […]
The post Is chocolate better than exercise for the brain? appeared first on OUPblog.

By: Elizabeth Gorney,
on 3/1/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
personality,
*Featured,
Science & Medicine,
Health & Medicine,
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Your Brain on Food,
amotivational syndrome,
Gary L. Wenk,
How Chemicals Control your Thoughts and Feeling,
Books,
smoking,
marijuana,
weed,
Add a tag
Does marijuana produce an amotivational syndrome? Whether the amotivational syndrome exists or not is still controversial; there are still too few poorly controlled small studies that don't allow a definitive answer. Most people who use marijuana don't develop this syndrome.
The post Does marijuana produce an amotivational syndrome? appeared first on OUPblog.

By: Alice,
on 11/18/2014
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
vape,
Word of the Year 2014,
WOTY2014,
e-cigarette,
Marijuana Legalization,
Books,
marijuana,
Word of the Year,
WOTY,
What Everyone Needs to Know,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Health & Medicine,
WENTK,
Jonathan P. Caulkins,
THC,
Add a tag
Oxford Dictionaries has selected vape as Word of the Year 2014, so we asked several experts to comment on the growth of electronic cigarettes and the vaping phenomenon.
Vape is a fascinating Word of the Year. Not only is the word new and important, but so is the actual activity. That’s different from merely coining a cute new label for a longstanding practice.
First, some clarification. Various drugs can be “smoked” or “vaporized”. Smoking involves combustion, as in “Where there is smoke, there is fire.” By contrast, when something is vaporized it is heated – using heat from an external source – to volatilize the molecules. Water vapor is the familiar example; steam is not produced by burning water.
The distinction matters for many drugs. Burning cocaine decomposes it into byproducts that are not psychoactive. Vaporized cocaine base is crack.
Burning tobacco releases smoke that is full of not only nicotine but also carcinogens. The nicotine is addictive but not carcinogenic. E-cigarettes provide the nicotine – and nicotine addiction – without those tars or hot gasses. (Nicotine evaporates at a much lower temperature than is created when tobacco burns.)
It’s not that e-cigarettes are healthy. Constant dosing with nicotine is bad for your heart. However, compared to the most deadly consumer product in history, e-cigarettes aren’t as bad. When I polled a number of medical colleagues, their best guesses – and they stressed at this point they are only guesses – were that all things considered, e-cigarettes will kill at something like one-tenth the rate per year of use as do conventional cigarettes. That could make e-cigarettes a life saver – unless they become a new gateway to nicotine addiction for adolescents who later convert to combusted tobacco products.
With marijuana, people traditionally mostly smoked the flowering tops (“buds”) of the cannabis plant in a joint (cigarette) or bong (water pipe). However, the recent liberalization of marijuana policy has made consumption of THC “extracts” more common. (You can also vape buds, but the trend is toward concentrates.)
Vaping is a boon to both the old tobacco and the new marijuana industries because it solves their fundamental problem: how to ensure long-term demand when these days almost no mature adult initiates use of a new dependence-inducing psychoactive. The vast majority of people who smoke tobacco or marijuana start before the age of 21; indeed, usually by age 16. Kids know cigarettes are deadly, and have lagged in the recent upsurge in marijuana use.
Cue the cavalry to the rescue in the form of all these fruit flavors, such as bubble gum, caramel candy, root beer, and mango, that appeal to kids. Originally tobacco companies were indifferent to e-cigarettes. Originally they were used mostly by established smokers, and it wasn’t clear whether they were more of an aid for those quitting (akin to nicotine gum) or a way to retain smokers by making hours spent in smoke-free restaurants and workplaces more tolerable.
The marijuana industry was not similarly conflicted because much of the THC in a cannabis plant is locked up in leaves and other parts that are not desirable in today’s market as “usable marijuana”. It has always been technically possible to extract that THC, but doing so efficiently requires a moderately large extraction machine – something whose presence used to be difficult to explain to the police or nosy neighbors. But once producing marijuana products became legal (albeit still only under state law), there were no qualms about owning an extraction machine and recovering all that additional THC.
Cheap THC extraction created a new problem: how to sell it to a marketplace that was focused on joints and bongs. A certain amount could be baked into brownies, mixed into beverages or ointments, or sold as dabs to hardcore users, but the killer app was vape pens. Vape pens are close to odorless, letting kids use at home without their parents knowing; they are easy to flavor; and they create an element of style. The same creativity that went into filling head shops with endless variations on the basic bong has been channeled into vape pens with features such as puff counters, batteries that plug into USB ports, and LED temperature indicators, as well as styling features ranging from classy gold plate to ninja turtle figurines and Snoop Dog endorsements.
The word vape itself is also key to this transformation. The scary word cigarette is part of the phrase e-cigarette, but vaping is new, chic, and as-of-yet decoupled from associations with cancer and heart disease.
All of this has made vaping trendy in a way it hadn’t been when e-cigarettes first hit the market, and now the big tobacco companies are jumping in with both feet, buying up small e-cigarette companies and putting their marketing muscle behind the trend. They smell opportunity; whereas it is illegal to flavor tobacco, there is no barrier to marketing kid-friendly fruit-flavored nicotine for e-cigarettes.
What remains to be seen is how the industry will evolve if and when marijuana is legalized nationwide. Will tobacco companies buy out the still small marijuana firms? Will they – or the marijuana companies – sell cartridges that come with nicotine and THC premixed? Or will this vaping fad disappear like a puff of vapor?
Hard to say. But right now, vape is the Word of Year.
The post Vaping in the old tobacco and new marijuana industries appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Julie Fergus,
on 4/20/2014
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Books,
plant,
marijuana,
pot,
420,
*Featured,
chemicals,
Science & Medicine,
Health & Medicine,
receptors,
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Cannabis indica,
CBD,
compounds in marijuana,
Gary Wenk,
How Chemicals Control,
national pot day,
THC,
Your Brain on Food,
Your Thoughts and Feelings,
wenk,
cannabinoid,
endogenous,
Add a tag
By Gary Wenk
Marijuana is the leafy material from Cannabis indica plant that is generally smoked. By weight, it typically contains 2%-5% delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive agent. However the plant also contains about fifty other cannabinoid-based compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD).
One Internet ad claims that “cannabidiol (CBD) can cure arthritis, multiple sclerosis, chronic pain, schizophrenia, and epilepsy.” CBD is the main non-psychotropic cannabinoid present in the Cannabis sativa plant, constituting up to 40% of its extract. Somehow this one particular component of the marijuana plant has become much more popular than all of the sixty (at least) other biologically active molecules that have been isolated from this plant, to the point where growers are breeding marijuana plants with significantly higher levels of CBD.

Why are people so excited about CBD? The answer lies in unpacking a series of complex truths, making distinctions between what is known and what is not known, and dispelling some false claims.
The human brain naturally possesses a pair of protein receptors that respond to endogenous marijuana-like chemicals. These receptors are incredibly common and are found throughout the human brain. When a person smokes marijuana, all of the various chemicals in the plant are inhaled, ultimately, into the brain where they find and bind to these receptors, similar to a key fitting into a lock. Which receptors are affected, and what parts of the brain are involved, differs for just about everyone, depending upon their genetic make-up, drug-taking history, and expectations regarding the experience; the last factor being commonly known as the placebo effect.
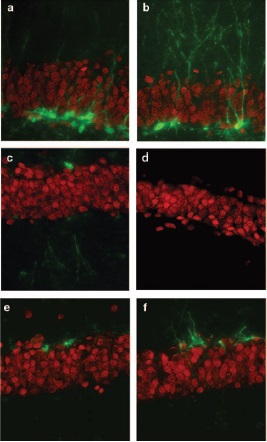
The images above come from Dr. Wenk’s research at Ohio State University, and demonstrate an increase in hippocampus neuron activity in rats following a cannabinoid treatment.
In addition, the chemicals inhaled into the brain also interact with a complex array of other neural systems; these interactions also contribute to the overall psychoactive experience, such as the marijuana’s ability to reduce anxiety, produce euphoria, or induce “the munchies.” My own research has demonstrated the positive effects of stimulation of the endogenous cannabinoid neural system in the aging brain.
Both CBD and THC are capable of interacting with this complex variety of proteins. However, and this is where things get interesting, they do not do so with the same degree of effectiveness. Scientists have shown that THC is over one thousand times more potent than is CBD, meaning a person would need to consume 1,000 “joints” of the genetically modified CDB-marijuana plant to get high. This chemical property of CBD has led to the accurate claim that CBD does not make one feel “high.” However, the low potency of CBD may also indicate that, by itself, it offers limited clinical benefits – currently- no one knows. Animal studies have discovered many beneficial effects of CBD but only when administered at very high doses.
What has become quite apparent is that no single component of the plant is entirely good or bad, therapeutic or harmful, or deserving of our complete attention. To date, all of the positive evidence supporting the use of medical marijuana in humans has come from studies of the entire plant or experimental investigations of THC. Given the very low potency of CBD within the brain it is highly unlikely that CBD alone will provide significant clinical benefit. Some small clinical trials are being initiated; until rigorous scientific studies are completed no one can claim that CBD is better than THC.
Gary L. Wenk, PhD., a Professor of Psychology & Neuroscience & Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics at the Ohio State University and Medical Center, is a leading authority on the consequences of chronic brain inflammation and animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. He is also the author of Your Brain on Food: How Chemicals Control Your Thoughts and Feelings.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only health and medicine articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image Credit: First image is from United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons.
The post Is CBD better than THC?: exploring compounds in marijuana appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 4/20/2014
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
four twenty,
cannabis,
*Featured,
Science & Medicine,
Health & Medicine,
Psychology & Neuroscience,
Colorado pot legalization,
Costs of Prohibition,
Maryland criminal penalties,
Mitch Earleywine,
Pot Politics,
Scientific Evidence,
Understanding Marijuana,
Washington pot legalization,
metabolites,
hemp,
earleywine,
recreational,
Books,
marijuana,
Add a tag
By Mitch Earleywine
A lot has changed this year in cannabis prohibition. Science and policy march on. Legendary legalization laws in Colorado and Washington have generated astounding news coverage. Maryland is the latest state to change policies. A look at these states can reveal a lot about the research on relevant topics, too.
Colorado and Taxes
Colorado provides taxed and regulated access to recreational users for the first time since 1937’s Marijuana Tax Act. Money rolls into the state’s coffers (roughly $3.4 million in January and February) and the sky has yet to fall. Some observers grouse that the taxes on the recreational market are not generating as much as pundits predicted, as if economic wonks have never guessed wrong before. Apparently, fewer medical users switched from their medical sources to the recreational suppliers. Given that the tax on medical cannabis is 2.9% and the recreational sources cost an additional 25%, we shouldn’t be stunned. It’s nice to see that people behave rationally. It’s only been a few months (since 1 January 2014), but the anticipated spikes in emergency room visits, psychotic breaks, and teen use are nowhere to be found.
Washington and DUI
Washington State continues to hammer out details for how their legal market will work. A per se driving law there has generated controversy. All 50 states prohibit driving while impaired after using cannabis, but the majority require prosecutors to prove recent use and unsafe operation. In contrast, these per se laws essentially make it illegal to drive with a specified amount of cannabis metabolites in the blood. Perfectly competent, safe drivers with the specified amount of metabolites are still breaking the law. For Washington State, the specified amount is 5ng/ml. Unfortunately, this level does not say much about actual impairment and laws like these don’t decrease traffic fatalities. Medical users, who often have more than the specified amount of metabolites, are particularly worried. Though they have developed tolerance to the plant with frequent use and likely show fine driving skill, they remain open for arrest. Plenty of prescription and over-the-counter medications have the potential to impair driving, but comparable laws for these drugs are not on the books. Given the potential for biased enforcement, per se laws like these will undoubtedly face challenges. Standard roadside sobriety tests like those used for alcohol, though less than perfect, might be fairer.

Maryland and Rising Change
A few days ago, the governor of Maryland signed bills removing criminal penalties for possession of small amounts of cannabis and setting up medical distribution. Citizens there caught with 10 grams of the plant risk arrest, a criminal record, a $500 fine, and up to 90 days in jail. After 1 October 2014, they’ll get slapped with a $100 fine for their first offense. Decriminalization can mean different things in different states, especially given the varied styles of police enforcement in each area. But comparable laws appear in Alaska, Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Mississippi, Nebraska, New York, North Carolina, and others. These laws have the potential to free up law enforcement time to decrease serious crimes.
Maryland will also become the 21st medical cannabis state. Over a third of the US population lives in states with medical cannabis laws now, but the details of distribution remain perplexing. Markedly fewer have access than this statistic would imply. Medical marijuana laws have provided the plant for the sickest of the sick, but without increasing teen use. They also appear to decrease traffic fatalities, perhaps by decreasing alcohol consumption. Medical marijuana laws appear to lower suicide rates in men by 5%, perhaps also via the impact on drinking.
Reaching the Public
A Pew Poll earlier this month suggests that data like these and changes in state laws accompany altered public opinion.
More people than ever (52%) support a legal market in the plant. Less than ¼ think possession should lead to jail time. Over 60% think that alcohol is more dangerous than cannabis. With attitudes like these, comparisons to the repeal of alcohol prohibition are loud and numerous. Though no one has a crystal ball and it’s impossible to guess the implications of policies that haven’t been around long, everyone agrees we’re in for an informative and wild ride in the years ahead.
Mitch Earleywine, Ph.D. is Associate Professor of Clinical Science and Director of Clinical Training in Psychology at the University of Southern California. He is the author of Pot Politics: Marijuana and the Costs of Prohibition and Understanding Marijuana: A New Look at the Scientific Evidence. He has received nine teaching awards for his courses on drugs and human behavior and is a leading researcher in psychology and addictions. He is Associate Editor of The Behavior Therapist.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only science and medicine articles the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Bush of a hemp. Lowryder 2. © Yarygin via iStockphoto.
The post The 4/20 update appeared first on OUPblog.


By: ChloeF,
on 2/8/2013
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
History,
African American Studies,
African,
VSI,
Values,
society,
marijuana,
jamaica,
very short Introductions,
heritage,
divine,
*Featured,
Rastafari,
western values,
VSIs,
downpression,
ecological backlash,
Ennis B. Edmonds,
Rasta,
Rastafarian,
rastas,
Add a tag
By Ennis B. Edmonds
Recently, I was discussing my academic interest with an acquaintance from my elementary school days. On revealing that I have researched and written about the Rastafarian movement, I was greeted with a look of incredulity. He followed this look with a question: “How has Rastafari assisted anyone to progress in life?” My friend assured me he was aware that prominent and accomplished Rastas exist in Jamaica, however he was convinced that Rastafari did not contribute to the social and economic mobility of most of its adherents. Sensing that my friend was espousing a notion of progress based on rising social status and increasing economic resources — reflecting his own journey from a peasant farming family to an elementary school teacher to a highly regarded principal of a number of schools to an educational officer at present — I pointed out that Rastafari rejects this conventional notion of progress, especially when it is for a few at the exclusion of the many. Pointing out that I had no understanding of Rastafari until I started researching it, I left hoping that next time he engages in a conversation on Rastafari, he will do so with greater understanding and appreciation.
Unfortunately, my acquaintance’s attitude towards Rastafari is widely shared by those who judge progress and personal worth by social mobility and increasing material resources within a Western cultural f ramework. Conversely, Rastafari has articulated a trenchant critique of Western values and institutions, asserting that they are based on exploitation and oppression of both humans and the environment. Western values and institutions have sown seeds of discord, distrust, and conflict that translate into social disharmony and all the social ills that plague contemporary societies. The rapacious exploitation of natural resources in pursuit of profit have violated sound ecological principles and will ultimately trigger an ecological backlash (are we already experiencing this in changing weather patterns?). In this respect, Rastafari is an implicit call for us to examine the foundation on which our political, economic, and cultural institutions and values are constructed. Are they designed to cater to the interest of the whole human family or the interest of those who monopolize and manipulate power? Are they informed by a desire to live in harmony with other humans and nature or by a desire to dominate both?
ramework. Conversely, Rastafari has articulated a trenchant critique of Western values and institutions, asserting that they are based on exploitation and oppression of both humans and the environment. Western values and institutions have sown seeds of discord, distrust, and conflict that translate into social disharmony and all the social ills that plague contemporary societies. The rapacious exploitation of natural resources in pursuit of profit have violated sound ecological principles and will ultimately trigger an ecological backlash (are we already experiencing this in changing weather patterns?). In this respect, Rastafari is an implicit call for us to examine the foundation on which our political, economic, and cultural institutions and values are constructed. Are they designed to cater to the interest of the whole human family or the interest of those who monopolize and manipulate power? Are they informed by a desire to live in harmony with other humans and nature or by a desire to dominate both?
But Rastafari is much more than a critique of Western society; it is a fashioning of an identity grounded in a sense of the human relationship to the Divine and to the African heritage of most of its adherents. Thus for Rastas, the Divine is not just some transcendent, ethereal being, but an essential essence in all humans and a cosmic presence that pervades the universe. To be Rasta is to be awakened to one’s innate divine essence and to strive to live one’s life in harmony with the divine principles that govern the world, instead of living like “baldheads” (non-Rastas) who are sometimes driven to excess in their pursuit of ego-satisfaction. On a more cultural level, Rastafari seeks to cultivate for its adherents an identity and a lifestyle based on a re-appropriation on an African past. Rejecting the slave and post-slavery identity foisted upon them by colonial powers, early Rastas and their successors turned to their African heritage to reconstitute their cultural selves. Despite the derogation of Africa and the denigration of Africans in colonial discourse, Rastas proudly affirm themselves as Africans and posit that an African sense of spirituality that embraces communality and living in harmony with the forces of nature is not only in line with divine principles, but also makes for a more harmonious relationship among humans and a more sustainable future for the earth.
Many of us approach Rastafari from a sense of curiosity inspired by the dramatic imagery that dreadlocks present, rumours we have heard about the copious use of ganja (marijuana) by its adherents, or the realization that the enchanting rhythms and conscious lyrics of reggae are Rasta-inspired. However, a closer look will make us realize that Rastafari presents us with a perspective that can help us ask questions about the mainstream values and institutions of Western society and beyond. Do these values and institutions promote freedom, justice, harmony, opportunity, and sustainability? Long before the Arab Spring and the Occupy Movement, Rastafari has been criticizing the “downpression,” inequities, and unsustainability of the political and economic structures of the world. How about how we regard our human selves? Are we just cogs in the wheel of an economic machine? Or do we have intrinsic value that is enhanced by living in harmony with other humans and our natural environment? You need not embrace Rastafari to appreciate Marley’s lyrics from “Survival”:
Click here to view the embedded video.
“In this age of technological inhumanity/Scientific atrocity/Atomic misphilosophy/Nuclear misenergy/It’s a world that forces lifelong insecurity.” Part of the liner notes from the album of the same name points the way out of this state of affairs: “But to live as one, equal in the eyes of the Almighty.”
Ennis B. Edmonds is Assistant Professor of African-American Religions and American Religions at Kenyon College, Ohio. His areas of expertise are African Diaspora Religions, Religion in America, and Sociology of Religion. His research has focused primarily on Rastafari, leading to Rastafari: From Outcasts to Culture Bearers and Rastafari: A Very Short Introduction.
The Very Short Introductions (VSI) series combines a small format with authoritative analysis and big ideas for hundreds of topic areas. Written by our expert authors, these books can change the way you think about the things that interest you and are the perfect introduction to subjects you previously knew nothing about. Grow your knowledge with OUPblog and the VSI series every Friday and like Very Short Introductions on Facebook.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only VSI articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Judah Lion, By Weweje [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
The post Appreciating the perspective of Rastafari appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/19/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Current Affairs,
drug abuse,
Colorado,
marijuana,
washington,
drug policy,
What Everyone Needs To Know,
federal government,
drug trafficking,
federal law,
*Featured,
Law & Politics,
DEA,
WENTK,
Angela Hawken,
Drug Enforcement Agency,
Jonathan P. Caulkins,
Mark A.R. Kleiman,
state law,
Add a tag
By Jonathan P. Caulkins, Angela Hawken, and Mark A.R. Kleiman
As officials in Washington State and Colorado try to decide how to implement the marijuana-legalization laws passed by their voters last month, officials in Washington, DC, are trying to figure out how to respond. Below, a quick guide to what’s at stake.
WHAT DO THE WASHINGTON AND COLORADO LAWS SAY?
Lots of crucial details remain to be determined, but in outline:
In both states, adults may — according to state but not federal law — possess limited amounts of marijuana, effective immediately.
In both states, there are to be licensed (and taxed) growers and sellers, under rules to take effect later this year.
Sales to minors and possession by minors remain illegal.
Colorado, but not Washington, now allows anyone person over the age of 21 to grow up to six marijuana plants (no more than three of them in the flowering stage) in any “enclosed, locked space,” and to store the marijuana so produced at the growing location. That marijuana can be given away (up to an ounce at a time), but not sold.
HOW MUCH OF THIS CAN THE FEDERAL GOVERNMENT PREVENT?
Paradoxically, the regulated activity permitted by these laws is easy to stop, but the unregulated activity is hard to stop.
Although everything allowed by the new state laws remains forbidden by federal law, if thousands of Coloradans start growing six pot plants each in their basements there wouldn’t be enough DEA agents to ferret them out. The same applies to possession for personal use.
On the other hand, the federal government has ample legal authority to shut down the proposed systems of state-licensed production and sale. Once someone formally applies to Colorado or Washington for permission to commit what remains a federal felony, a federal court can enjoin that person from doing any such thing, and such orders are easily enforced. So the federal government could make it impossible to act as a licensed grower or seller in either state.
Moreover, it could do so at any time. The lists of license-holders will always be available, and at any point they could be enjoined from continuing to act under those licenses. That creates a “wait-and-see” option unusual in law enforcement situations; in general, an illicit activity becomes harder to suppress the larger it is and the longer it has been established.
WHAT IMPACT WILL THE LAWS HAVE ON DRUG ABUSE?
It is possible that removing the state-level legal liability for possession and use of marijuana will increase demand, but there is little historical evidence from other jurisdictions that changing user penalties much affects consumption patterns.
There is no historical evidence concerning how legal production and sale might influence consumption, for the simple reason that no modern jurisdiction has ever allowed large-scale commercial production. But commercialization might matter more than mere legality of use. It could affect consumption by making drugs easier to get, by making them cheaper, by improving quality and reliability as perceived by consumers, and by changing attitudes: both consumer attitudes toward the drugs and the attitudes of others about those who use drugs. How great the impacts would be remains to be seen; it would depend in part on yet-to-be-determined details of the Colorado and Washington systems.
Washington’s legislation is designed to keep the price of legally-sold marijuana about the same as the current price of illegal marijuana. Colorado’s system might allow substantially lower prices. Falling prices would be expected to have a significant impact on consumption, especially among very heavy users and users with limited disposable income: the poor and the young.
WHAT EFFECT WILL THE LAWS HAVE ON DRUG TRAFFICKING?
If the laws affect Mexican drug trafficking organizations at all, the impact will be to deprive them of some, but not the bulk, of their revenues. Transnational drug trafficking organizations currently profiting from smuggling marijuana into the US or organizing its production here cannot gain from increased competition.
The open question is how much, if any, revenue they would lose from either falling prices or reduced market share. The oft-cited figure that the big Mexican drug trafficking groups derive 60% of their drug-export revenue from marijuana trafficking has been thoroughly debunked; the true figure is closer to 25%, and that doesn’t count their ill-gotten gains from domestic Mexican drug dealing or from extortion, kidnapping, and theft. So don’t expect Los Zetas to go out of business, whatever happens in Colorado.
Legal marijuana in Washington State is likely to be too expensive to compete on the national market. But prices in Colorado might be low enough to make legal cannabis from Colorado retailers competitive with illicit sellers of wholesale cannabis as a supply for marijuana dealers in other states. To take advantage of that opportunity, out-of-state dealers could organize groups of “smurfs” to buy one ounce each at multiple retail outlets; a provision of the Colorado law forbids the state from collecting the sort of information about buyers that might discourage smurfing. Marijuana prices might fall substantially nationwide, with harmful impacts on drug abuse but beneficial impacts on international trafficking. (The state government could even gain revenue if Colorado became a national source of marijuana.)
The other wild card in the deck is the Colorado “home-grow” provision. Marijuana producers in Colorado will be able to grow the plant without any risk of enforcement action by the state, and also without any registration requirement or taxation, as long as they grow no more than three flowering plants and three plants not yet in flower at any given location. By developing networks of grow locations each below the legal limit, entrepreneurs could create large-scale production operations with a significant cost advantage over states where growing must be concealed from state and local law enforcement agencies.
Only time will tell whether Colorado “home-grown” could compete with California and Canada in the national and international market for high-potency cannabis or with Mexico in the market for “commercial-grade” cannabis. But the risks imposed by local law enforcement, and the costs of concealment to avoid those risks, constitute such a large share of the costs of illegal marijuana growing that avoiding those costs would constitute a very great competitive advantage, and illicit enterprise has proven highly adaptable to changing conditions.
IS THERE A BASIS FOR A BARGAIN?
Maybe. Federal and state authorities share an interest in preventing the development of large interstate sales from Colorado and Washington, and the whole country might gain from learning about the experience of legalization in those two states: as long as the effects of those laws could be mostly contained within those states. The question is whether the federal government might be willing to let Colorado and Washington try allowing in-state sales while working hard to prevent exports, and whether those states, with federal help (and the threat of a federal crackdown on their licensed growers and sellers if Washington and Colorado product started to show up in New York and Texas), could succeed in doing so. If that happens, it would be vital to have mechanisms in place to learn as much as possible from the experiment.
Things will get even more complex if other states decide to join the party.
So buckle your seat belts; this could be a rather bumpy ride.
Mark A.R. Kleiman, Jonathan P. Caulkins, and Angela Hawken are the authors of Drugs and Drug Policy: What Everyone Needs to Know. Mark A.R. Kleiman is Professor of Public Policy at UCLA, editor of The Journal of Drug Policy Analysis, and author of When Brute Force Fails and Against Excess. Jonathan P. Caulkins is Stever Professor of Operations Research and Public Policy at Carnegie Mellon University. Angela Hawken is Associate Professor of Public Policy at Pepperdine University.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only law and politics articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Semi-legal marijuana in Colorado and Washington: what comes next? appeared first on OUPblog.

5. Right Livelihood
Right livelihood means that one should earn one's living in a righteous way and that wealth should be gained legally and peacefully. The Buddha mentions four specific activities that harm other beings and that one should avoid for this reason: 1. dealing in weapons, 2. dealing in living beings (including raising animals for slaughter as well as slave trade and prostitution), 3. working in meat production and butchery, and 4. selling intoxicants and poisons, such as alcohol and drugs. Furthermore any other occupation that would violate the principles of right speech and right action should be avoided.
These days I'm earning my livelihood primarily by way of my retirement benefits from Social Security and a small pension from That Insurance Company for which I worked. I also work a number of part-time jobs. I edit books, screenplays, stage plays, and other materials; I work as a patient model (also known as a standardized patient) once in a great while; I dogsit for a select clientele; and even more rarely, I catsit. I write almost every day of the year, but that doesn't bring in a lot of dough. Still, it definitely meets the criteria of Right Livelihood: it is legal, peaceful, and righteous. I harm no one with my writing, as I do my best to write as I speak, aiming to hurt no one.
There are many people my age who are resorting to selling their prescriptions in order to buy food or pay their mortgages. A person can understand how one can be driven to desperate thinking. But if one is living a Buddhist life, one cannot consider that type of livelihood, any more than working for the OLCC, or working as a meat wrapper for Fred Meyer, or a butcher for Whole Foods. A job as a bartender, or cocktail waiter would also violate the principles of right livelihood for a Buddhist. As would working at a place that sells medicinal marijuana, I think. And I think this because I believe that people choose to stay there to use the marijuana. If people picked up their drugs as they do from a pharmacy and left, that would be a different matter. As a person who lives with pain on a regular basis, I feel no need or desire to socialize with other sufferers while I take my medicine and seek relief. Therefore, I don't understand why medical marijuana users need a socializing area either. I believe this hurts the cause. Well, that was a tangent. I could be wrong. Seriously though, people who need and receive morphine for their pain, do not need a cafe in which to "enjoy" their morphine. They pick it up or have it delivered, and get relief. Period. Why wouldn't marijuana be the same when used for the same purpose?

By: Lauren,
on 10/25/2010
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
A-Featured,
drugs,
marijuana,
weed,
pot,
cannabis,
get high,
marcello pennacchio,
medical marijuana,
pharmaceuticals,
Health,
Law,
Politics,
Add a tag
By Marcello Pennacchio
Few plants have generated as much debate and controversy as cannabis (Cannabis sativa). Throughout the ages, it has been labelled both a dangerous drug and potent medicine. Where the former is concerned, law-enforcement agents and governments spend millions of dollars fighting what many consider to be a losing battle, while fortunes are being pocketed by those who sell it illegally. This is in spite of the fact that cannabis produces a number of natural pharmacologically-active substances, the medicinal potential of which were recognized thousands of years ago. Chinese Emperor, Shên Nung, for example, prescribed cannabis elixirs for a variety of illnesses as early as 3000 BC. It was equally prized as a medicine in other ancient civilisations, including India, Egypt, Assyria, Palestine, Judea and Rome and may have been instrumental in helping Ancient Greece’s Delphian Oracle during her divinations.
While its more common contemporary uses are mostly recreational, cannabis continues to enjoy widespread use as a medicine. It is smoked to ease glaucoma, to help with the degenerative loss of condition and body mass associated with diseases such as HIV/AIDS, and it helps to ease chronic pain in people suffering from terminal cancers and other debilitating illnesses. It has been used for treating malaria, gout, multiple sclerosis, eating disorders, promoting euphoria, as well as for dispelling grief and sorrow. A number of serious side effects have also been linked to its use, however. These include heart problems, immune system suppression, cancer, depression, reduced cognitive function and poor fetal development. It can lead to a variety of psychological problems, too, such as psychosis and schizophrenia, as well as to addiction to this and other drugs. Then there is the added danger of inhaling dangerous chemicals generated during the combustion of organic matter. Chief among these are carbon monoxide and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
With so many pros and cons, it’s easy to see why the issue of cannabis has so significantly polarized sentiment around the world. Those in favour of its use want it legalized, with perhaps its most vocal advocates being in San Francisco. This is where one of the world’s first universities dedicated solely to cannabis, is located. Founded in 2007 by Richard Lee, Oaksterdam University was inspired by a similar college in Amsterdam and has since spread to include campuses elsewhere in California and in Michigan. So passionate are its founders and students about cannabis that they have taken the debate of legalizing it all the way to California’s November 2, 2010, ballot, a move that has since made world headlines. Many had hoped a similar proposal in Florida, known as the Medical Marijuana Initiative, would have made it into that state’s ballot, too, but the petition failed to gather the 700, 000 signatures required for it to qualify. Florida’s four-year rolling petition system means, however, that it may qualify for the 2012 ballot.
Surprisingly, the push to legalize cannabis includes former judges, politicians and other high-profile people, many of who themselves don’t use cannabis (including this author). They believe that penalizing and incarcerating its users is far more detrimental to them than smoking its parts are. They further contend that legalizing and taxing cannabis would raise significant revenue for governments. It would also alleviate the enormous drain of cash reserves needed to police its illegal use and, in the process, eliminate the criminal syndicates that sell it. Furthermore, they claim it would ensure that the quality of the product meets stringent regulations.
These are all convincing arguments, but it is difficult for many of us to get around the fact that smoking cannabis, a
 Oh My--Self-Published Picture Book Down with the P-O-T...
Oh My--Self-Published Picture Book Down with the P-O-T...
Take a look at this disturbingly hilarious (hilariously disturbing?) post on Galley Cat about a self-published picture book called It's Just a Plant (which I'm not linking to. OK yes I am--because you can click through and read this fine piece of literature ***), "an illustrated children's book about marijuana" that is "a book for parents who want to educate their children about the complexities of pot in a thoughtful, fact-oriented manner."
The commentary about the book from the former publisher of High Time magazine is, well, commentary from the former publisher of High Times. Dude.
*** in English, Finnish, German, Hungarian, Korean, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish or Thai. I kid you not. And don't miss the reviews (one of which calls the author "the Dr. Seuss of pot") from the likes of Entertainment Weekly, Bill O'Reilly, and David Crosby.








If you have some works that you would like to get published, find out how easy it is to self-publish @ http://click.linksynergy.com/fs-bin/click?id=d5KderlsEio&offerid=139411.10000005&type=3&subid=0