new posts in all blogs
Viewing: Blog Posts Tagged with: mars, Most Recent at Top [Help]
Results 1 - 25 of 31
How to use this Page
You are viewing the most recent posts tagged with the words: mars in the JacketFlap blog reader. What is a tag? Think of a tag as a keyword or category label. Tags can both help you find posts on JacketFlap.com as well as provide an easy way for you to "remember" and classify posts for later recall. Try adding a tag yourself by clicking "Add a tag" below a post's header. Scroll down through the list of Recent Posts in the left column and click on a post title that sounds interesting. You can view all posts from a specific blog by clicking the Blog name in the right column, or you can click a 'More Posts from this Blog' link in any individual post.

By: Franca Driessen,
on 2/9/2016
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
global warming,
mars,
space exploration,
planets,
universe,
astronauts,
solar system,
Pluto,
*Featured,
Physics & Chemistry,
Science & Medicine,
humankind,
life on earth,
blue planets,
cataclysm,
Exploring the Planets,
Fred Taylor,
planetary exploration,
Technological Innovation,
the future of earth,
Books,
Add a tag
The Earth we live on was formed from a cloud of dust and ice, heated by a massive ball of compressed hydrogen that was the early Sun. Somewhere along the four billion year journey to where we are today, our planet acquired life, and some of that became us. Our modern brains ask how it all came together and progressed, and what shaped the pathways it followed.
The post Blue planet blues appeared first on OUPblog.

By:
[email protected],
on 10/28/2015
Blog:
Perpetually Adolescent
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Movie Adaptation,
Book Reviews - Fiction,
andy weir,
the martian.,
Tracey Allen,
science fiction,
movies,
Book News,
science,
space,
mars,
Matt Damon,
Ridley Scott,
Add a tag
The Martian by Andy Weir has a fabulous back story. Initially published chapter by chapter and made available for free on the author’s website, readers soon fell in love with the story. First, they asked him to make it available as an ebook, so they could enjoy it on their e-readers rather than having to read it […]

By: Yasmin Coonjah,
on 10/10/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Books,
space,
mars,
planets,
Water,
Mark Williams,
Pluto,
Jan Zalasiewicz,
*Featured,
Science & Medicine,
gale crater,
Earth & Life Sciences,
Ocean Worlds,
water on mars,
space technology,
The story of seas on Earth and other planets,
yellowknife lake,
Add a tag
The story of our Solar System is developing into one of the most absorbing – and puzzling – epics of contemporary science. At the heart of it lies one of the greatest questions of all – just how special is our own planet, which teems with life and (this is the difficult bit) which has teemed with life continuously through most of its 4.5 billion year lifetime? Not all of the answers are to be found here on Earth.
The post Mars, Pluto… and beyond appeared first on OUPblog.

By: KatherineS,
on 10/9/2015
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
water on mars,
science,
space,
Moon,
mars,
NASA,
planets,
Water,
astronomy,
VSI,
physics,
Very Short Introductions,
Phoenix,
A Very Short Introduction,
Editor's Picks,
*Featured,
Physics & Chemistry,
Science & Medicine,
david rothery,
Earth & Life Sciences,
VSI online,
Moons: A Very Short Introduction,
calcium perchlorate,
Planets: A Very Short Intoduction,
Add a tag
The discovery of water on Mars has been claimed so often that I’d forgive anyone for being skeptical about the latest announcement. Frozen water, ice, has been proven on Mars in many places, there are lots of ancient canyons hundreds of kilometres long that must have been carved by rivers, and much smaller gullies that are evidently much younger.
The post NASA discovers water on Mars again: take it with a pinch of salt appeared first on OUPblog.
 So yesterday I started composing in my head what I wanted to say about Andy Weir’s The Martian and I was working up a good post too until I realized I had homework to attend to! Poof went all my mental work. Crud. The homework was writing and submitting my Library Journal review on Frida Kahlo’s Garden. I can only submit reviews between 175-200 words and they have very specific requirements. Every word counts. It isn’t so very hard to write it now that I’ve gotten good practice at it. However, it doesn’t leave time to write that blog post either. Having begun writing that blog post in my head and getting on with it pretty well, do you think I might remember any of it? Ha! Ha! Ha! Of course not! That’s why there’s this excuse of an introduction. And unfortunately I had no mental dreaming time at work today to begin again so I begin now and we’ll see where this goes.
So yesterday I started composing in my head what I wanted to say about Andy Weir’s The Martian and I was working up a good post too until I realized I had homework to attend to! Poof went all my mental work. Crud. The homework was writing and submitting my Library Journal review on Frida Kahlo’s Garden. I can only submit reviews between 175-200 words and they have very specific requirements. Every word counts. It isn’t so very hard to write it now that I’ve gotten good practice at it. However, it doesn’t leave time to write that blog post either. Having begun writing that blog post in my head and getting on with it pretty well, do you think I might remember any of it? Ha! Ha! Ha! Of course not! That’s why there’s this excuse of an introduction. And unfortunately I had no mental dreaming time at work today to begin again so I begin now and we’ll see where this goes.
The Martian. Loved it. Laugh out loud funny at times. Mark Watney’s smartass humor is what helps him survive alone on Mars and that’s saying something because I don’t think many of us would find any kind of humor in being left for dead on Mars by your crewmates in an emergency evacuation during a major dust storm. And he doesn’t even have a radio with which to contact NASA. Talk about being completely and utterly alone. So he begins recording a log of his days and the things he has to do to survive. He is a botanist and an engineer, two skill sets that turn out to be really helpful as he has to repair things that break and jury-rig other equipment to make them do things they were not designed to do. He also has to figure out how to grow food because there is not enough astronaut food for him to survive the four years he is going to be there.
The book is Watney’s log but it also jumps around a bit so we get the story told through the perspective of NASA as well as the crew who left him behind. Here is an example of some of the humor. NASA has just realized Watney is alive and given a news conference. Two of the people in charge of the program are talking and we get this:
‘I wonder what he’s thinking right now.’
LOG ENTRY: SOL 61
How come Aquaman can control whales? They’re mammals! Makes no sense.
The pacing is great. There are many tense moments especially getting towards the end when something really bad happens. I was reading that part on the plane Sunday afternoon and I had a momentary mental fit: dammit! He better not die! If he dies I’m going to be really pissed! Weir wouldn’t do that would he? Take him so far just to kill him? He’s not George R.R. Martin. Please don’t be like George R.R. Martin!
There was actually another event so very close to the end that precipitated another similar outburst. These outbursts had to be mental you see because I was already in trouble for attempting to bring some very dangerous hummus onto the plane. I didn’t want to give them any reason to escort me somewhere when the plane landed.
I don’t think it is spoiler to say the book has a “happy” ending. If it is, I’m sorry to have just given it away.
Weir originally published the book chapter by chapter on his blog. He is one of those uber-geeks who spends his free time learning about relativistic physics and orbital mechanics. But in this case it is good because he began daydreaming about what-if Mars scenarios and it turned into a book with very accurate science. The book was so popular his readers asked him to make it available as an ebook. So Weir formatted it and published it on Amazon for .99 cents because Amazon wouldn’t let him give it away for free. It became such a success that he was approached by a publisher and the rest, as they say, is history. But between the Amazon publication and the print publication Weir received numerous letters from scientists kindly correcting his errors and Weir made corrections to the book accordingly before print publication. While we have not gone to Mars yet, NASA has a Mars program plan called Mars Direct and Weir used this as the basis for his book.
The book touched all kinds of buttons in my geeky heart; space travel, real science that not once relies on some made up magical science to save the day, funny, suspenseful, surprising and unabashedly entertaining. Also, if it were me stuck on Mars, I’d be so dead. Therefore, when the day arrives when humans do actually go to Mars, you will not find me standing in line for a chance to go. I’ll keep my feet firmly planted here on Earth, thank you very much.
Filed under:
Books,
Reviews Tagged:
Andy Weir,
Mars 


By: Stacy A. Nyikos,
on 4/1/2014
Blog:
Stacy A. Nyikos
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Science Fiction,
Star Trek,
Star Wars,
space,
Mars,
Frankenstein,
Tor,
Mary Shelley,
Andy Weir,
The Martian,
Add a tag
The MartianAndy Weir
Science Fiction - Adult
Pop quiz:
1) Do you ever stare at the night sky wondering if there is life out there?
2) Ever tried to levitate something with your mind?
3) Have you ever secretly (or not so secretly) watch Star Trek?
Houston, we have lift off. You like science fiction!
Science fiction has been fascinating readers from the moment Mary Shelley brought Frankenstein's monster to life. And writers of science fiction have been working to keep their edge ever since that first breath of life into their genre. Today, they're getting a little help from actual, real life physicists. Science fiction has become your basic rocket science.
How can this be? Some brilliant people at Tor had the great idea to pair up science fiction writers with NASA scientists. The result is a new list of science fiction titles, headed up by Andy Weir's,
The Martian.
Basic premise: Robinson Crusoe on Mars.
More details: Mark Watney, a member of the Ares 3 Mars crew, accidentally gets left on Mars during the middle of a sandstorm. He has a habitat. He has oxygen and water. He has some food. But he doesn't have enough to last until the next Ares mission arrives. Cue creativity. How will Mark survive? Will NASA be able to help?
Weir's characters are wonderfully diverse and wickedly smart without being so smart they become inaccessible. The plot is scary believable. Accidents can happen, especially on a mission to a place as far away and foreign as Mars. The scientific does not way down the story, but rather, enhance it. Admittedly, there were moments when I did zone a little. Then again, that could have been the elliptical machine getting the better of me. I have books I "save" for work outs only. This was one. But I found myself sneaking more of
The Martian whenever I could, like a secret stash of chocolate. And more than once that I had to remind myself this is NOT REAL. It's "just" a story (so stop crying!).
Tor has more books in the line up. One is about an elevator from earth to the international space station. Finally, a true fix for my science fiction addiction. I can't wait to see what they imagine up next. And...um...if it's not too much to ask, does anyone know how to get in the super secret society of writers who get to work with these amazing scientists?
For more April fling reads, check out
Barrie Summy's website!

By:
[email protected],
on 3/27/2014
Blog:
Perpetually Adolescent
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Books,
science fiction,
fiction,
space,
sci-fi,
survival,
mars,
NASA,
stranded,
survival story,
castaway,
Book Reviews - Fiction,
andy weir,
astronaught,
manned mission to Mars,
Mark Watney,
the martian.,
Add a tag
 This was of the funnest books I can remember reading in a long time. Gripping, funny and told in a totally original and authentic voice you can’t help but be hooked in by this part-Apollo 13, part-Castaway survival story.
This was of the funnest books I can remember reading in a long time. Gripping, funny and told in a totally original and authentic voice you can’t help but be hooked in by this part-Apollo 13, part-Castaway survival story.
Mark Watney is an astronaut, part of the third manned mission to Mars. Six days after landing on Mars a fierce dust storm forces Mark and his crewmates to abandon the planet. However during the evacuation Mark is left behind. Now he must work out how is going to survive on Mars until the next resupply mission. In two years time.
The majority of the book is told via Mark’s log entries detailing his survival. The log is written in a beautifully sarcastic tone where outright panic is only a hair’s breath away. There is plenty of self-deprecating humour and the log format works perfectly in detailing Mark’s day-to-day survival.
Mark is completely stranded. He has no way of communicating with his crewmates or NASA. He only has enough food and water to last half the time he needs. Mark puts to work his skills as an engineer and botanist to figure out if he can survive. The how is one of the most entertaining reads you will come across. Full of insane (but practical) problem solving you are glued to the book wanting to find out how Mark gets himself out of each new predicament he finds himself in. I defy anyone to be able to put this down once they start!
Buy the book here…

By: Mark Miller,
on 6/27/2013
Blog:
From the land of Empyrean
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
science fiction,
middle grade,
math,
science,
Mars,
young reader,
authors in the park,
Jean E. Lane,
JLB Creatives,
Add a tag
My friend and fellow JLB Creatives team member, Jean E. Lane, has a delightful book called Lill and Mewe and the Secrets of Mars. Well, I got a chance to read it after a rave review from my 12 year old daughter - she said it was a must read. I wanted to share my thoughts with my own short review.
Charming in its simplicity, yet surprisingly complex. There is a lot going on with this fun little story. The author has some big ideas and writes for her target audience. The secrets of Mars are revealed with a civilization hidden beneath the surface of the red planet. The focus of the story is on Lill, her younger brother and their insatiable curiosity. The story ends piquing my curiosity and leaves me ready for the sequel. Like a good series should, this first book comes to a satisfying end, but leaves the reader with a few questions. This story is perfect for middle grade and some young readers, especially if they are interested in fun and science!
About the book: When Lill, a young Martian girl, receives a telescope for her birthday and locates planet Earth, she and her water cat, Mewe, "borrow" a new space craft called the Whisper 5 and travel to Earth, where they meet a girl named Lily. Back on Mars, Lill looks for her brother Merak, who, also on a mission, has lost contact when his warp drive safety failed and may have left the galaxy. Lill later learns Merak was rescued, but by whom? As Lill watches Mewe's swim race at Frogscry River, where she competes with the other water cats, Lill discovers a glowing orb in the wall of a cave. The orb holds the thoughts of Martians who have died hundreds of years ago, along with ancient wisdom. What will she learn from the orb? Will she find Merak? What are the secrets of the history of Mars? Follow the exciting adventures of Lill and Mewe as they seek answers in a world of advanced computers, androids and artificial intelligence.
About the author: Jean E. Lane is originally from Youngstown, Ohio. She now lives in Orlando, FL with her husband Kenneth, their energetic dog Prancer, and two curious cats: Muffy and Abby.
She has worked most of her life in logistics, financial accounting, and purchasing. Her true interest lies in the almost believable aliens of the classic science fiction stories she enjoyed growing up.
Skygazing is a hobby which led her write her first children's novel, Lill and Mewe and the Secrets of Mars, the first of the Lill and Mewe series.
She uses math, science, discovery, learning, humor, and adventure in her books. But don't be scared...the math and science are great for kids ages 8 -12. Adults appreciate the content being that her writing style is highly entertaining while delivering facts so their children so they can learn while having fun.
You can get the paperback here:
His name is John Carter!
You can follow him, my girl cat Mars (Marceline the Vampire Queen) and her biological brother (and nemesis, apparently) Barnaby, on
Instagram at
#marsandbarsandcars (@
frootjoos)
For now, I'm off to make him another batch of kitten formula :/ he's so little he can't feed himself yet!
 The Mighty Mars Rovers: The Incredible Adventures of Spirit and Opportunity Elizabeth Rusch
The Mighty Mars Rovers: The Incredible Adventures of Spirit and Opportunity Elizabeth Rusch
I'm back looking at more the books on YALSA's Excellence in Nonfiction for Young Adults long-list.
This is another great addition to the always excellent Scientists in the Field series. Steven Squyres is a geologist who wanted to study the rocks on Mars. He came up with the idea to send a robotic geologist in his place. The Mars Rovers went up in 2003. Spirit and Opportunity were supposed to last about 3 months. They lasted for years. Opportunity is *still* going and doing science.
I really enjoyed the way the book follows the Rovers and the team on Earth. It does a great job of showing how the scientists on the ground had to often quickly build a "fake Mars" to figure out if there was a way they could get a rover out a jam-- up a hill, or out of a sand dune. It's also so well that I almost cried when Spirit went quiet. No little robot who's lasted years longer than you should, don't die!
It also does a great job of explaining why this type of exploration is important and why we're so obsessed with studying Mars.
You can follow the Mars Rovers on NASA's website.
Update: I forgot to link to today's Nonfiction Monday roundup! It's at Perogie's and Gyoza.
Book Provided by... the publisher, for award consideration.
Links to Amazon are an affiliate link. You can help support Biblio File by purchasing any item (not just the one linked to!) through these links. Read my full disclosure statement.

By: Alice,
on 2/6/2013
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Dictionaries,
monkey,
mars,
etymology,
anatoly liberman,
mare,
*Featured,
Lexicography & Language,
better,
gobelet,
word origins,
monthly gleanings,
Overused Words,
vaso,
Add a tag
By Anatoly Liberman
I am picking up where I left off a week ago.
Mare and Mars. Can they be related?
The chance is close to zero. Both words are of obscure origin, and attempts to explain an opaque word by referring it to an equally opaque one invariably come out wrong. Although Mars, the name of the Roman war god, has been compared with the Greek verb márnamai “I fight,” this comparison may be the product of folk etymology. Some festivals dedicated to Mars involved horses, but the connection was not direct. Since the success of campaigns depended on the good state of chariots, war and steeds formed a natural union. Mare has multiple Germanic and Celtic cognates. However, it may be a migratory word of Eastern origin. For example, Russian merin “gelding” has almost the same root. A similar case is Latin caballus “packhorse; nag,” later just “horse” and Russian kobyla “mare” (stress on the second syllable).
Monkey.
Along the same lines, I must defer judgment with regard to the word for “monkey” in Arabic, Farsi, and Romany. At the end of my post on monkey, I suggested that we might be dealing with a migratory animal name. If I am right, the etymology of one more hard word will be partly clarified.
Better.
In the post on suppletive forms, I wrote that better is the comparative of a nonexistent positive degree (good has a different root).The question from our correspondent concerned Farsi beh, behtar, behtarin. Are those forms related to better? Not being a specialist in Indo-Iranian, I cannot answer this question. (However, if h is a separate phoneme belonging to the root, the relation is unlikely.) I will only say that better is akin to Engl. boot in to boot and bootless (all such cognates refer to gain and improvement) and that the standard etymological dictionaries of Indo-European (Walde-Pokorny and Pokorny) mention only Sanskrit and Avestan congeners of better (Gothic batiza); they mean “happy.”
En gobelet (French) ~ en vaso (Spanish).
These phrases designate a vine pruned to the shape of a hollow cup. Was the drinking vessel named after the shape of the vine, or was the shape of the vine named after the drinking vessel? I am sure the second variant is correct.
Overused Words
As noted last time, I received a sizable list of words that the listeners of Minnesota Public radio “hate.” It is an instructive list. I also have my peeves. For example, I wince every time I hear that so-and so is a Renaissance man. In some circles, it suffices to know the correct spelling of principle and principal to become an equal of Leonardo. Fascinating is another enemy, and so is the cutting edge (in academia, to be on the cutting edge, one has to be interdisciplinary). Nothing is nowadays good, acceptable, or proper: the maid of all work is sustainable: sustainable behavior, sustainable budget, sustainable tourism—every quality and object has its sustainable niche (rhyming in the Midwest and perhaps everywhere with kitsch, witch, and bitch). Some of my “enemies” are pretentious Latinisms. For instance, I never accepted utilize outside its technical context (use is good enough for me) and morph for “change.” Why should things morph instead of changing? And why do students hope to utilize my notes? Do they want to recycle them?
I began to pay attention to other buzzwords only after they were pointed out to me:
Amazing.
True enough, newspapers and TV find themselves constantly enraptured. Their frame of mind is one of permanent astonishment and wonderment: the simplest things amaze them: a readable book, cold weather, and even cheap pizza. As a result, amazing has come to mean “worthy of notice.” It followed the same “trajectory” as Renaissance man. Rather scary are also the adjectives epic and surreal. The protagonists of epic poetry are larger than life, but with us every important event acquires “epic” dimensions. Likewise, though reality is full of surprises, every unexpected situation need not be called surreal.
Trajectory.
The word has been worked to death. Path, road, way, development, direction, and the rest have yielded to it. This holds for journalists and speech writers at all levels. President Obama: “I think Ronald Reagan changed the trajectory of America in a way that Richard Nixon did not and in a way that Bill Clinton did not.”
Impact.
This word has killed influence and its synonyms. I remember the time when the concerned guardians of English usage fought the verb impact. Now both the verb and the noun have become the un-words of the decade. Everything “has an impact” and “impacts” its neighbors. Impact is a tolerably good word, but, like chocolate, it cloys the appetite and produces heartburn if consumed in great quantities.
I will now quote some of the messages I received. Perhaps our correspondents will comment on them:
Dialogue.
“I absolutely hate dialogue used as verb, as in let’s dialogue about that. Also hate go-to as in it’s my go-to snack or it’s my go-to workout.” Both do sound silly, for go-to (never a beauty) originated in contexts like this is the person to go to (= turn to) if you need good advice. Shakespeare would have been puzzled: in his days go to was a transparent euphemism for go to the devil. As for dialogue, it has succumbed to the powerful rule that has “impacted” English since at least the sixteenth century: every noun, and not only nouns, can be converted into a verb (consider “but me no buts,” “if ifs and buts were candy and nuts,” and the like). Sometimes the opposite process occurs: meet is a verb, and meet, a noun, came into being. It does not follow that we should admire the verb dialogue.
Folks.
“My least favorite word… when politicians use the word folks, like they are intimately familiar with their audience.” I agree! Folks should not be used as a doublet of folk.
Clearly.
“Whenever so-called experts weigh in on news stories, they preface their statements with the word clearly. Clearly somehow makes whatever they say irrefutably true.”
Actually.
“…count the number of times the word is used in a culture of growing mistrust of analysts and experts who make predictions about news before it happens…” I have waged a losing war against such adverbs (actually, really, clearly, definitely, certainly, doubtlessly) for years, but actually is the worst offender, a symptom of what I call advanced adverbialitis (–Where were you born? –Actually, I was born in California.)
Doubling down.
“The one I started hearing a lot this year is ‘So-and-so is doubling down on [a provocative statement or position]. Holy cow, political commentators, what did you do before this phrase crawled into your brains!” I guess they were milking some other venerable cow, possibly unrelated to gambling.
Evolve.
There was a complaint about the use of the verb evolve as meaning “develop; change” (“…so many people describe themselves or their opinions as ‘evolving’….”). In the past, I resented devolve as a synonym of degenerate, because I had been using this verb only in contexts like “I devolved all authority to my assistant,” but gradually accepted the other sense. By now I have heard evolve “change” so many times that it no longer irritates me (unlike morph).
Organic/natural.
In my talk show, I said that I am tired of hearing that nearly everything I buy is called organic or natural and was reprimanded: “There are strict standards set by government for the term organic, while the term natural is not regulated. You are maligning the organic food industry by proffering the incorrect information.” I stand corrected and apologize.
Random.
One of the listeners resented the promiscuous use of the adjective random (the epithet above is mine). Mr. Dan Kolz wrote in a letter to me: “In programming circles, a random value is one generated by the computer which is not predictable or predefined by the programmer. It can be used like: ‘I found a bug in test which generated random values as parameters’. It is sometimes used as a synonym for arbitrary or in a longer form ‘an arbitrarily chosen value’. This indicates that from the programmer’s perspective the value was unpredictable (if not actually from the user’s). It is in this sense that the word random could have acquired the meaning ‘selected or determined for no reason I know or could have predicted’, as in ‘I went to the party, but there were just a bunch of random people there’.” This strikes me as a reasonable explanation. Computer talk has really (clearly and actually) had a strong influence on Modern English. For instance, cross out and expunge have disappeared from the language: everything is now “deleted.”
May I repeat my old request? Sometimes people discover an old post of mine and leave a comment there. I have no chance to find it. Always leave your comments in the space allotted to the most recent posts. Above, I rejected a connection between mare and Mars. By way of compensation, you will see an equestrian print of the Roman war god, though I suspect that his horses were chargers rather than mares.
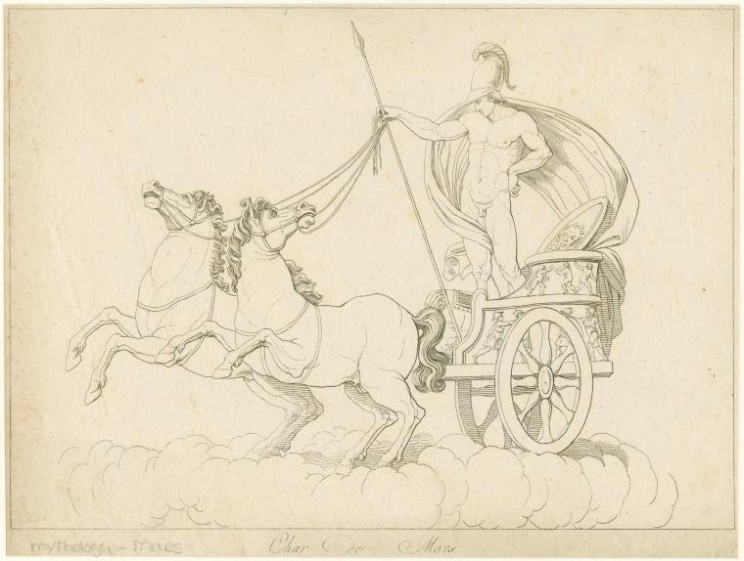

Char de Mars. Engraving. Wonders: Images of the Ancient World / Mythology — Mars. Source: NYPL.
 Anatoly Liberman is the author of Word Origins…And How We Know Them as well as An Analytic Dictionary of English Etymology: An Introduction. His column on word origins, The Oxford Etymologist, appears here, each Wednesday. Send your etymology question to him care of [email protected]; he’ll do his best to avoid responding with “origin unknown.”
Anatoly Liberman is the author of Word Origins…And How We Know Them as well as An Analytic Dictionary of English Etymology: An Introduction. His column on word origins, The Oxford Etymologist, appears here, each Wednesday. Send your etymology question to him care of [email protected]; he’ll do his best to avoid responding with “origin unknown.”
Subscribe to Anatoly Liberman’s weekly etymology posts via email or RSS.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Monthly etymology gleanings for January 2013, part 2 appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/10/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Current Affairs,
Geography,
mars,
place of the year,
POTY,
extraterrestrial,
Social Sciences,
Editor's Picks,
*Featured,
Law & Politics,
outer,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
Gérardine Goh Escolar,
Max Planck Encyclopedia of Public International Law,
grubby,
Add a tag
By Gérardine Goh Escolar
The relentless heat of the sun waned quickly as it slipped below the horizon. All around, ochre, crimson and scarlet rock glowed, the brief burning embers of a dying day. Clouds of red dust rose from the unseen depths of the dry canyon — Mars? I wish! We were hiking in the Grand Canyon, on vacation in that part of our world so like its red sister. It was 5 August 2012. And what was a space lawyer to do while on vacation in the Grand Canyon that day? Why, attend the Grand Canyon NASA Curiosity event, of course!
Wait, what? Space lawyers? Have they got their grubby hands on Mars now?
Well, quite the contrary, and in a manner of speaking, space law has been working to keep any grubby hands off Mars. In the heady aftermath of the Soviet launch of Sputnik-1 in 1957, nations flocked to the United Nations to discuss — and rapidly agree upon — the basic principles relating to outer space. Just a decade later, the 1967 Outer Space Treaty was concluded, declaring outer space a global commons, and establishing that the “exploration and use of outer space shall be carried on for the benefit and in the interests of all mankind”. Today, more than half of the world’s nations are Parties to the Outer Space Treaty, and its principles have achieved that hallowed status of international law — custom — meaning that they are binding on all States, Party or not.
More specifically, the 1967 Outer Space Treaty affirmed that outer space, including the Moon, planets, and other natural objects in outer space (such as Mars!), were not subject to appropriation, forbidding States from claiming any property rights over them. Enterprising companies and individuals have sought to exploit what they saw as a loophole in the Treaty, laying claim to extraterrestrial land on the Moon, Mars and beyond, and selling acres of this extraterrestrial property for a pretty penny. One company claims to have sold over 300 million acres of the Moon to more than 5 million people in 176 countries since 1980. The price of one Moon acre from this company starts at USD$29.99 (not including a deep 10% discount for the holiday season) — potentially making the owner of said company a very rich man. Other companies have also started a differentiated pricing model: “The Moon on a Budget” – only USD$18.95 per acre if you wouldn’t mind a view of the Sea of Vapours — vs. the “premiere lunar location” of the Sea of Tranquillity for USD$37.50 per acre. The package includes a “beautifully engraved parchment deed, a satellite photograph of the property and an information sheet detailing the geography of your region of the moon.” Land on Mars comes at a premium: starting at USD$26.97 per acre, or a “VIP” deal of USD$151.38 for 10 Mars acres.
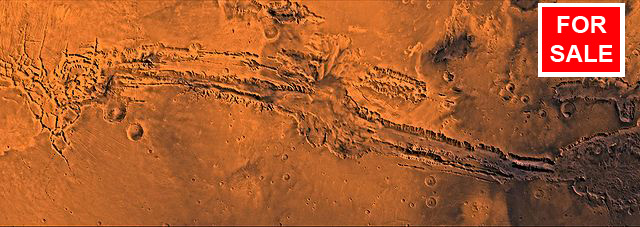
Indeed, the USD$18.95 may be a good price for the paper that the “beautifully engraved parchment deed” is printed on. And that is likely all you will get for your money. Although the Treaty does not also explicitly forbid individuals or corporate entities from laying claim to extraterrestrial property, it does make States internationally responsible for space activities carried out by their nationals. Despite these companies’ belief that the Treaty only prohibits States from appropriating extraterrestrial property, it is disingenuous to say that on Mars and any other natural object in outer space, “apart from the laws of the HEAD CHEESE, currently no law exists.” International law does apply to the use and exploration of outer space and natural extraterrestrial bodies, including Mars. And that international law, including the prohibition on the appropriation of extraterrestrial property, applies equally to individuals and corporate entities through the vehicle of State responsibility in international law, and through domestic enforcement procedures.
Now, that’s not to say that the principle of non-appropriation is popular. It has been questioned by a caucus of concerned publicists, worried that it would stifle commercial interest in the exploration of Mars. Some other publicists — myself included — have come up with proposals for “fair trade/eco”-type uses of outer space that they contend should be an exception to the blanket ban. But the law at the moment stands as it is — Mars cannot be owned. Or bought. Or sold. For many private ventures into outer space, that is a “big legal buzzkill.” These days, it seems, NASA may even land a spacecraft on the asteroid you purport to own and refuse to pay parking charges — and the US federal court will actually dismiss your case as without legal merit. What is the world coming to?
On the bright side, international space law has meant that there has been a lot of international cooperation in outer space. This has mostly kept the peace in outer space (no Star Wars!) and has ensured the freedom of the exploration and use of outer space for the benefit of humanity. International space law has also contributed towards keeping the Martian (and outer space) environment pristine. And in a world where we worry about the future of our own blue planet, maybe having international law keep our grubby hands of her sister Red Planet isn’t such a bad idea after all.
Dr. Gérardine Goh Escolar is Associate Legal Officer at the United Nations. She is also Associate Research Fellow at the International Institute of Air and Space Law at Leiden University, and has taught international law and space law at various universities, including the National University of Singapore, the University of Cologne and the University of Bonn. She was formerly legal officer and project manager at a national space agency, as well as counsel for a satellite-geoinformation data company. She is currently working on her fourth book, International Law and Outer Space (Oxford International Law Library, OUP: forthcoming 2014). All opinions and any errors in this post are entirely her own.
The Max Planck Encyclopedia of Public International Law is a comprehensive online resource containing peer-reviewed articles on every aspect of public international law. Written and edited by an incomparable team of over 800 scholars and practitioners, published in partnership with the Max Planck Institute for Comparative Public Law and International Law, and updated through-out the year, this major reference work is essential for anyone researching or teaching international law. Articles on outer space law, free for a limited time, include: “Moon and Celestial Bodies” ; “Astronauts” ; “Outer Space, Liability for Damage” ; and “Spacecraft, Satellites, and Space Objects”.
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year competition, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World – the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only law and politics articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Valles Marineris is a vast canyon system that runs along the Martian equator. Courtesy NASA/JPL-Caltech/USGS. Image has been altered from the original with the addition of a “FOR SALE” sign.
The post Mars, grubby hands, and international law appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/9/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Geography,
mars,
oed,
odnb,
American National Biography,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
ANB,
oxfod english dictionary,
Oxford Reference,
oxford companion,
who's who,
Oxford Index,
oxford dictionary national biography,
oxford medicine,
Add a tag
By Alice Northover
With our announcement of Place of the Year 2012 and NASA’s announcement at the American Geophysical Union on December 3rd, and a week full of posts about Mars, what beter way to wrap things up than by pulling together information from across Oxford’s resources to provide some background on the Red Planet.
Of Gods and Men
While the planet been subject to study since humans first gazed into the sky (as one of the few planets visible to the naked eye), the English name for the planet comes from the Roman god of war, Mars. Latin marks many astronomical names, such as mare, which refers to the dark areas of the Moon or Mars. Sol (Latin for Sun) refers to a solar day on Mars (roughly 24 hours and 39 minutes). However, be careful not to mix up martialists, those born under its astrological influence, with martians, aliens from the planet. (Not that it always had that meaning.) Mars has two moons: Phobos and Deimos (those Latin names again!). The Romans, as usual, stole their planet-naming scheme from the Greeks. Ares, the Greek god of war, provides a pre-fix for a number of Mars-related words: areocentric, areˈographer, areo-graphic, are-ography, are’ology. It’s important to remember that these names reveal how people related, and continue to relate to the sky.
The Martian People
What has fueled our fascination with Mars all these years? Everyone from scientists to poets has kept it in our thoughts over the centuries.
Almost all ancient world cultures closely observed its pattern through the sky, although this was often a confluence of gods, astrology, and astronomy. Aristotle and Ptolemy were among the ancient theorists. The Renaissance saw new discoveries from Brahe, Kepler, and Cassini among others, made possible by the telescope and advanced mathematics, as we moved from a geocentric to a heliocentric view of the universe (although Mars’s eccentric orbit caused considerable annoyance).
In the 19th century, Giovanni Schiaparelli was the first to create a detailed map of Mars. Percival Lowell (1855-1916), who saw himself as a successor to Schiaparelli, searched for signs of intelligent life on Mars and made numerous invaluable observations, even if many of his speculations have now been dismissed. Moreover, his legacy, the Lowell Observatory, continues to watch the stars. Astronomer Richard Proctor (1837-88) researched the rotation period of Mars and rightly dismissed the canals as an optical effect.
Scientific breakthroughs naturally inspired artists throughout the ages. In the Renaissance, writers struggled to make sense of a new vision of the universe; in the 19th century, science fiction emerged and it has grown and adapted to every medium in the 20th. H.G. Wells (1866–1946) and Edgar Rice Burroughs (1875-1950) built on scientific discoveries with novels such as The War of the Worlds and The Princess of Mars. In 1938, Orson Welles’s (1915-1985) famous dramatization of The War of the Worlds led many Americans to believe that Martians had invaded New Jersey. The story was adapted to film in 1953 and again in 2005. One of the masterpieces of Soviet cinema, Aelita, is based on an Aleksey Tolstoy science fiction novel. In television, Mars has provided the backdrop or villians for numerous programs, such as the Ice Warriors, one of the great monsters of Doctor Who. UFOs still capture the imagination.
The planet has also provided ideas to musicians as diverse as Gustav Holst and David Bowie, and populated the night skies of artists. And we cannot forget those with the surname of Mars, most of all confectioners Frank C. Mars and Edward Forrest Mars (1904-1999). Mars, Inc. and the famous Mars Bar are often associated with the planet although the origin of their names is distinctly earthly.
A History of Martian Space Exploration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), Russian Federal Space Agency (ROSCOSMOS), and the European Space Agency (ESA) have all been involved in the exploration of Mars, from probes to rovers. In 1962 the Soviet space program began lanching Mars probes, the last of which was Mars 96 (in 1996). In 1975, NASA sent two Viking probes to Mars. In 1996, NASA begins a series of missions called Mars Surveyor and has sent numerous probes, rovers, and more to the Red Planet in the past 20 years, including the Mars Pathfinder (and the rover Sojourner), the Mars Odyssey, the Mars Global Surveyor, and two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity.
But space exploration is not without its setbacks. The Soviet Union failed in its Phobos missions in 1988, and NASA lost communication with the probe New Millennium Deep Space-2 in 1999. The European Space Agency’s Mars Express probe continues to provide valuable information although the Beagle 2 lander was lost.
The Mars Curiosity Rover landed successfully at 10:32 pm PST on 5 August 2012. But is it physically possible for us to send a human there? And how long would it take to get there and back?
Areography
There has been much speculation about the geography and geology of Mars, with new theories arising as our technology improves.
Mars is a terrestrial planet with numerous montes (mountain ranges), valles (valleys) , rima (long narrow furrows), and cave systems. Its most famous geographical features are the Olympus Mons (giant volcano) and Valles Marineris (system of canyons).
In the 19th and 20th centuries, people speculated about Martian canals, faint markings of the surface that once led people to believe the planet had flowing, liquid water. (The word canal actually comes from a mis-translation Giovanni Schiaparelli’s work; canali (Italian) actually means channels.) Wrinkle ridges further added to the mystery.
Without a thick atmosphere to burn up descending asteroids, Mars is pockmarked with impact craters. The Mars Curiosity Rover landed in the Gale Crater, just south of Mars’s equator. Previous rovers have attempted to measure Marsquakes, the Martian equivalent of earthquakes, as the Red Planet may have its own system of tectonic plates.
The Long Arm of Outer Space Law
In space, no one can hear you scream, but that doesn’t stop the lawsuit.
It began with the UN Declaration of Legal Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space in 1963 and the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies in 1967 because of the need to regulate competing claims on the shared space of outer space.
Who can claim land or natural resources in space? What are the health and safety provisions for astronauts? Under whose jurisdiction do they fall? Are you liable when your telecommunications satellite scrapes the International Space Station? Exactly who’s in charge of the space up there anyway? These are only a few of the questions legal scholars are grappling with.
What would we call our red planet lawmen? Marshals of course — although martial and marshal aren’t actually related. And be sure to check back tomorrow to hear from our space lawyer!
Recommended resources from A Dictionary of Space Exploration
The Mars Climate Database
The Mars Exploration Program
Views of the Solar System
Space Ref
And remember: Stay curious!
Alice Northover joined Oxford University Press as Social Media Manager in January 2012. She is editor of the OUPblog, constant tweeter @OUPAcademic, daily Facebooker at Oxford Academic, and Google Plus updater of Oxford Academic, amongst other things. You can learn more about her bizarre habits on the blog.
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World – the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only geography articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post An Oxford Companion to Mars appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/8/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
shakespeare,
Geography,
renaissance,
mars,
John Donne,
astrology,
astronomy,
marlowe,
place of the year,
Copernicus,
john evelyn,
galileo,
Humanities,
POTY,
Social Sciences,
Kepler,
Editor's Picks,
*Featured,
Middleton,
Oxford Scholarly Editions Online,
OSEO,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
Claude Mylon,
Francois de Verdus,
Gascoigne,
Girolamo Preti,
John Skelton,
Marilyn Deegan,
Robert Burton,
Samuel Sorbière,
Thomas Hobbes,
Thomas Stanley,
William Lilly,
Literature,
Add a tag
By Marilyn Deegan
The new discoveries of the Mars rover Curiosity have greatly excited the world in the last few weeks, and speculation was rife about whether some evidence of life has been found. (In actuality, Curiosity discovered complex chemistry, including organic compounds, in a Martian soil analysis.)
Why the excitement? Well, astronomy, cosmology, astrology, and all matters to do with the stars, the planets, the universe, and space have always fascinated humankind. Scientists, astrologers, soothsayers, and ordinary people look up to the heavenly bodies and wonder what is up there, how far away, whether there is life out there, and what influence these bodies have upon our lives and our fortunes. Were we born under a lucky star? Will our horoscope this week reveal our future? What is the composition of the planets?
Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences, but it was the invention of the telescope in the early 17th century that advanced astronomy into a science in the modern sense of the word. Throughout the course of the 16th and 17th centuries, Copernicus, Galileo, Kepler, and others challenged the established Ptolemeic cosmology, and put forth the theory of a heliocentric solar system. The Church found a heliocentric universe impossible to accept because medieval Christian cosmology placed earth at the centre of the universe with the Empyrean sphere or Paradise at the outer edge of the circle; in this model, the moral universe and the physical universe are inextricably linked. (This is a model that is typified in Dante’s Divine Comedy.)
Authors from John Skelton (1460-1529) to John Evelyn (1620-1706) lived in this same period of great change and discovery, and we find a great deal of evidence in Renaissance writings to show that the myths, legends, and scientific discoveries around astronomy were a significant source of inspiration.
The planets are of course not just planets: they are also personifications of the Greek and Roman gods; Mars is a warlike planet, named after the god of war. Because of its red colour the Babylonians saw it as an aggressive planet and had special ceremonies on a Tuesday (Mars’ day; mardi in French) to ward off its baleful influence. We find much evidence of the warlike nature of Mars in writers of the period: Thomas Stanley’s 1646 translation Love Triumphant from A Dialogue Written in Italian by Girolamo Preti (1582-1626) is a verbal battle between Venus and her accompanying personifications (Love, Beauty, Adonis) and Mars (who was one of her lovers) and his cohort concerning the superior powers of love and war. Venus wins out over the warlike Mars: a familiar image of the period.
John Lyly’s play The Woman in the Moon (c.1590-1595) also personifies the planets and plays on the traditional notion that there is a man in the moon. Lyly’s use of the planets is thought to reflect the Elizabethan penchant for horoscope casting. The warlike Mars versus Venus trope is common throughout the period, and it appears in the works of Shakespeare, Marlowe, Middleton, Gascoigne, and most of their contemporaries. A search in the current Oxford Scholarly Editions Online collection for Mars and Venus reveals almost 300 examples. Many writers of the period also refer to astrological predictions; Shakespeare in Sonnet 14 says:
Not from the stars do I my judgement pluck,
And yet methinks I have astronomy,
But not to tell of good or evil luck,
Of plagues, of dearths, or seasons’ quality;
This is thought to be a response to Philip Sidney’s quote in ‘Astrophil and Stella’ (26):
Who oft fore-judge my after-following race,
By only those two starres in Stella’s face.
Thomas Powell (1608-1660) suggests astrological allusions in his poem ‘Olor Iscanus’:
What Planet rul’d your birth? what wittie star?
That you so like in Souls as Bodies are!
…
Teach the Star-gazers, and delight their Eyes,
Being fixt a Constellation in the Skyes.
While there is still much myth and metaphor pertaining to heavenly bodies in 17th century literature, there is increasing scientific discussion of the positions of the planets and their motions. To give just a few examples, Robert Burton’s 1620 Anatomy of Melancholy discusses the new heliocentric theories of the planets and suggests that the period of revolution of Mars around the sun is around three years (in actuality it is two years).
In his Paradoxes and Problemes of 1633, John Donne in Probleme X discusses the relative distances of the planets from the earth and quotes Kepler:
Why Venus starre onely doth cast a Shadowe?
Is it because it is neerer the earth? But they whose profession it is to see that nothing bee donne in heaven without theyr consent (as Kepler sayes in himselfe of all Astrologers) have bidd Mercury to bee nearer.
The editor’s note suggests that Donne is following the Ptolemaic geocentric system rather than the recently proposed heliocentric system. In his Devotions upon Emergent Occasions of 1623 Donne castigates those who imagine that there are other peopled worlds, saying:
Men that inhere upon Nature only, are so far from thinking, that there is anything singular in this world, as that they will scarce thinke, that this world it selfe is singular, but that every Planet, and every Starre, is another world like this; They finde reason to conceive, not onely a pluralitie in every Species in the world, but a pluralitie of worlds;
There are also a number of letters written in the 1650s and 1660s between Thomas Hobbes and Claude Mylon, Francois de Verdus, and Samuel Sorbière concerning the geometry of planetary motion.
William Lilly’s chapter on Mars in his Christian Astrology (1647), is a blend of the scientific and the metaphoric. He is correct that Mars orbits the sun in around two years ‘one yeer 321 dayes, or thereabouts’, and he lists in great detail the attributes of Mars: the plants, sicknesses, qualities associated with the planet. And he states that among the other planets, Venus is his only friend.
There are few areas of knowledge where myth, metaphor, and science are as continuously connected as that pertaining to space and the universe. Our origins, our meaning systems, and our destinies — whatever our religious beliefs — are bound up with this unimaginably large emptiness, furnished with distant bodies that show us their lights, lights which may have been extinguished in actuality millenia ago. Only death is more mysterious, and many of our beliefs about life and death are also bound up with the mysteries of the universe. That is why we remain so fascinated with Mars.
Marilyn Deegan is Professor Emerita in the Department of Digital Humanities at King’s College, University of London. She has published widely on textual editing and digital imaging. Her book publications include Digital Futures: Strategies for the Information Age (with Simon Tanner, 2002), Digital Preservation (edited volume, with Simon Tanner, 2006), Text Editing, Print and the Digital World (edited volume, with Kathryn Sutherland, 2008), and Transferred Illusions: Digital Technology and the Forms of Print (with Kathryn Sutherland, 2009). She is editor of the journal Literary and Linguistics Computing and has worked on numerous digitization projects in the arts and humanities. Read Marilyn’s blog post where she looks at the evolution of electronic publishing.
Oxford Scholarly Editions Online (OSEO) is a major new publishing initiative from Oxford University Press. The launch content (as at September 2012) includes the complete text of more than 170 scholarly editions of material written between 1485 and 1660, including all of Shakespeare’s plays and the poetry of John Donne, opening up exciting new possibilities for research and comparison. The collection is set to grow into a massive virtual library, ultimately including the entirety of Oxford’s distinguished list of authoritative scholarly editions.
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World – the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only literature articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Written in the stars appeared first on OUPblog.


By: AlanaP,
on 12/7/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
science fiction,
Literature,
Geography,
mars,
VSI,
Seed,
very short Introductions,
wells,
place of the year,
Humanities,
Atlas of the World,
POTY,
War of the Worlds,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
VSIs,
david seed,
Add a tag

By David Seed
 Although there had been interest in Mars earlier, towards the end of the nineteenth century there was a sudden surge of novels describing travel to the red planet. One of the earliest was Percy Greg’s Across the Zodiac (1880) which set the pattern for early Mars fiction by framing its story as a manuscript found in a battered metal container. Greg obviously assumed that his readers would find the story incredible and sets up the discovery of the ‘record’, as he calls it, by a traveler to the USA to distance himself from the extraordinary events within the novel. The space traveler is an amateur scientist who has stumbled across a force in Nature he calls ‘apergy’ which conveniently makes it possible for him to travel to Mars in his spaceship. When he arrives there, he discovers that the planet is inhabited. Since then, the conviction that beings like ourselves live on Mars has constantly fed writings about the planet. The American astronomer Percival Lowell was one of the strongest advocates of the idea in his 1908 book Mars as the Abode of Life and in other pieces, some of which were read by the young H.G. Wells. Mars had the obvious attraction of opening up new sensational subjects. Greg’s astronaut modestly describes his story as the ‘most stupendous adventure’ in human history. It also resembled a colony.
Although there had been interest in Mars earlier, towards the end of the nineteenth century there was a sudden surge of novels describing travel to the red planet. One of the earliest was Percy Greg’s Across the Zodiac (1880) which set the pattern for early Mars fiction by framing its story as a manuscript found in a battered metal container. Greg obviously assumed that his readers would find the story incredible and sets up the discovery of the ‘record’, as he calls it, by a traveler to the USA to distance himself from the extraordinary events within the novel. The space traveler is an amateur scientist who has stumbled across a force in Nature he calls ‘apergy’ which conveniently makes it possible for him to travel to Mars in his spaceship. When he arrives there, he discovers that the planet is inhabited. Since then, the conviction that beings like ourselves live on Mars has constantly fed writings about the planet. The American astronomer Percival Lowell was one of the strongest advocates of the idea in his 1908 book Mars as the Abode of Life and in other pieces, some of which were read by the young H.G. Wells. Mars had the obvious attraction of opening up new sensational subjects. Greg’s astronaut modestly describes his story as the ‘most stupendous adventure’ in human history. It also resembled a colony.
It’s no coincidence that the surge of Mars fiction coincided with the peak of empire, so by this logic the red planet is sometimes imagined as a transposed other country. Gustavus W. Pope’s Journey to Mars (1894) describes the voyage of an American spacecraft to a utopian world of sophisticated civilization and technology. The Martians encountered by the travelers are immediately identified as allies and one of the climactic moments in the novel comes when they fly the American flag during a naval parade. The narrator is almost moved beyond words by the spectacle:
My eyes filled with tears of joy when I thought that, the banner of liberty which waves o’er the land of the free and the home of the brave, honoured in every nation and on every sea of Earth’s broad domain, should have been borne through the trackless realms of space, amid that shining galaxy of orbs that wheel around the sun, and UNFOLD ITS BROAD STRIPES AND BRIGHT STARS OVER ANOTHER WORLD!
Pope’s description is unusual in presenting the Martians as so similar to the travelers that they project hardly any sense of the alien and, even more important, seem quite happy for America to take the lead in the course of civilization.
 The most famous Mars novel from the turn of the twentieth century, H.G. Wells’ The War of the Worlds (1898), takes the British treatment of the Tasmanians as a notorious example of brutal imperialism and then simply reverses the terms. The invading Martians simply direct against the capital city of the British Empire the same crude logic of empire: we are technologically able to conquer you, so we will do so. What still gives an impressive force to Wells’ narrative is the journalistic care that he took to document the gradual collapse of England. Despite its army and navy, the state is helpless to resist the Martians and they are only defeated by the germs of Earth rather than by its technology.
The most famous Mars novel from the turn of the twentieth century, H.G. Wells’ The War of the Worlds (1898), takes the British treatment of the Tasmanians as a notorious example of brutal imperialism and then simply reverses the terms. The invading Martians simply direct against the capital city of the British Empire the same crude logic of empire: we are technologically able to conquer you, so we will do so. What still gives an impressive force to Wells’ narrative is the journalistic care that he took to document the gradual collapse of England. Despite its army and navy, the state is helpless to resist the Martians and they are only defeated by the germs of Earth rather than by its technology.

Cover of “Edison’s Conquest of Mars”, from 1898. Illustration by G. Y. Kauffman.
This story of collapse did not please the American astronomer Garrett P. Serviss, who immediately wrote a sequel, Edison’s Conquest of Mars. Rather than waiting passively for the Martians to return, as Wells warns they might in his coda, Serviss describes an expedition to conquer them on their home planet. Two steps have to be taken before this can be done. First, the American inventor Edison discovers the secrets of the Martians’ technology and devises a ‘disintegrator’, which will destroy its targets utterly. Secondly, the nations of the world have to chip in to the expedition with large donations. Serviss describes an amazingly unanimous global cooperation: “The United States naturally took the lead, and their leadership was never for a moment questioned abroad.” Put this narrative against the background of the USA taking over former Spanish colonies like Cuba and the Philippines, and Serviss’s narrative can be read as an idealized fantasy of America’s emerging imperial role in the world. Of course no conquest would be worthwhile if it came too easily and Serviss’s Martians aren’t the octopus-like creatures described by Wells, but instead represent human qualities and characteristics taken to inhuman lengths.
Empire was only one way of imagining Mars. It also offered itself as a hypothetical location for utopian speculation. This is how it functions in the Australian Joseph Fraser’s Melbourne and Mars (1889), whose subtitle — The Mysterious Life on Two Planets — indicates the author’s method of comparison. Similarly, Unveiling a Parallel, by Two Women of the West (1893), written by the Americans Alice Ingenfritz Jones and Ella Merchant, describes two alternative societies visited by a traveler from Earth. All Mars fiction tends to take for granted the technology of flight and the vehicle in this novel is an ‘aeroplane’, one of the earliest uses of the term. When the narrator lands on Mars he has no difficulty at all in adjustment or with the language, quite simply because Mars is not treated as an alien place so much as a forum for social change.
The most surprising characteristic of early Mars writing is its sheer variety. Sometimes the planet is imagined as a potential colony, sometimes as an alternative society, or as place for adventure. One of the strangest versions of the planet was given in the American natural scientist Louis Pope Gratacap’s 1903 book, The Certainty of a Future Life on Mars. The narrator’s father is a scientist researching into electricity and astronomy with a strong commitment to spiritualism. After he dies, the narrator starts receiving telegraphic messages from his father describing Mars as an idealized spiritual haven for the dead. It is typical of the period for Gratacap to combine science with religion in narrative that resembles a novel. Before we dismiss the idea of telegraphy here, it is worth remembering that the electrical experimenter Nikola Tesla published articles around 1900 on exactly this possibility of communicating electronically with Mars and other planets.
All the main early works on Mars are available on the web or have been reprinted. They make up a fascinating body of material which helps to explain where our perceptions of the red planet come from.
David Seed is Professor in the School of English, University of Liverpool. He is the author of Science Fiction: A Very Short Introduction.
The Very Short Introductions (VSI) series combines a small format with authoritative analysis and big ideas for hundreds of topic areas. Written by our expert authors, these books can change the way you think about the things that interest you and are the perfect introduction to subjects you previously knew nothing about. Grow your knowledge with OUPblog and the VSI series every Friday!
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year competition, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World — the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only literature articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: War of the Worlds’ 1st edition cover.
The post The discovery of Mars in literature appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/6/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Music,
Geography,
mars,
gmo,
oxford music online,
place of the year,
OMO,
POTY,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Arts & Leisure,
Grove Music Online,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
Claudio Monteverdi,
Gustav Holst,
Kyle Gann,
Add a tag
By Kyle Gann
By long tradition, sweet Venus and mystical Neptune are the planets astrologically connected with music. The relevance of Mars, “the bringer of war” as one famous composition has it, would seem to be pretty oblique. Mars in the horoscope has to do with action, ego, how we separate ourselves off from the world; it is “the fighting principle for the Sun,” in the words of famous astrologer Liz Greene. Michel Gauquelin, who conducted a statistical test for the validity of astrology, found that Mars near the ascendant or midheaven in a person’s chart correlated heavily with choosing athletics or surgery as a career: it connects to physical competition and knives. Mars also rules everything military, and thus in music it is associated mainly with percussion. Most composers have egos, but musicians are not generally a physically aggressive bunch, and fighting isn’t our area. Many a famous composer sat out World War II playing in the Army band. (In high school I was thrilled that my simply taking music classes exempted me from the gym requirement — under the institutional assumption that all music students would get enough exercise in the marching band. I was a pianist.)

Claudio Monteverdi
And so Mars, in the classical music world, has been only an occasional acquaintance. There isn’t much classical music about athletics, though Arthur Honegger did write a rather punchy tone poem called
Rugby (1928), and Charles Ives — a star baseball player in youth — portrayed a
Yale-Princeton Football Game in music around 1899 as a kind of college prank. Music specifically about surgery may have yet to appear (and let’s leave Salomé out of this). Seeking a connection between Mars and music,
Gustav Holst would probably leap to most minds, but I think first of
Claudio Monteverdi. Holst, after all, had to give all his planets equal treatment, but it was Monteverdi who invented the “stile concitato,” the agitated style, to restore in music what he saw as a warlike mode known in poetry but historically absent in music. He made his theories explicit in his scenic cantata
Il combattimento di Tancredi e Clorinda of 1624, its poem a kind of forced sexual encounter disguised as a battle between armed rivals. Monteverdi makes it quite clear what he considered warlike tones:
lots of quick repeated notes in a harmonic stasis. And if you think about it, that description applies equally well to
“Mars” from Holst’s Planets (1914–16), with its hammering, one-note ostinato, and, as we’ll see below, to most other battle pieces as well. Considering the phenomenal evolution of the actual military, its musical signifiers have remained strikingly consistent.
Despite Monteverdi’s continued advocacy in some subsequent Madrigali guerrieri of 1638, the stile concitato did not establish itself as a broad genre. In the centuries following Il combattimento, depiction of martial action is rare enough in music for the well-known instances to be easily enumerated. The first of Johann Kuhnau’s Biblical History sonatas (1700) purports to describe David’s conflict with Goliath, once again with a profusion of quick repeated notes; also with “martial” rhythms such as streams of dotted eighths followed by sixteenths, or the snare-drum rhythm of an eighth and two sixteenths. The Battalia a 9 (1673) of Heinrich Ignaz Franz von Biber is for only strings, but it too makes a fetish of chords in repeated notes. Its “Der Mars” movement, in addition, brilliantly asks for a piece of paper between the fingerboard and strings of the cello to make the instrument’s rhythmic drone sound plausibly like some kind of drum. Michel Corrette’s Combat Naval from his Harpsichord Divertimento No. 2 (1779) likewise starts off with repeated notes in snare-drum rhythms, and climaxes with forearm clusters that quite effectively signify cannon blasts. In Mozart’s and Haydn’s generations, even the presence of drums and cymbals was enough to suggest Turkish and thus military connotations (since what were the Turks there for, except to make war with?), as in Haydn’s “Military” Symphony, No. 100.
The advent of Romanticism, though, marked a turn at which war became demoted as a subject for serious musical treatment. Two of the 19th century’s most high-profile musical depictions — Beethoven’s Wellington’s Victory (1813) and Liszt’s Hunnenschlacht (1857) — are considered among their most embarrassingly literal and superficial works. Bruckner did claim that the Plutonian finale of his Eighth Symphony (1887) depicted two emperors meeting on the field of battle, but that was rather after the fact, since he was trying to throw his lot in among the programmaticists. All this suggests, I think, distinct unease among classical musicians with things military or violent. Of course military music is sometimes appropriated to good effect, as in Berlioz’s Rakoczy March from The Damnation of Faust (1846). But despite Monteverdi’s heroic attempt to establish a martial mode, in retrospect classical attempts to depict battle tend to become anomalous oddities from history (Corrette, Biber) or humorous superficialities (Beethoven, Liszt).

Carl Nielsen
Finally, in the 20th century, the increase in dissonance and percussion brought at least a more respectable realism to battle music, though the carnage of the World Wars made anti-war statements more popular than celebrations of famous victories.
Carl Nielsen’s Fifth Symphony (1922) was a powerful response to the lunacy of World War I, with a first movement in which a solo snare drum seems determined to halt the progress of the orchestra, whose humanistic main theme finally overwhelms it. A couple of conflagrations later, Stravinsky made an anti-war statement in his
Symphony in Three Movements (1945), partly inspired by film images of goose-stepping Nazi soldiers. Less ironically, George Antheil cheered the Allies along with his
Fifth Symphony, subtitled “1942” and written that year as the fortunes of war were changing in North Africa. Shostakovich, in his
Leningrad Symphony (1941), wrote melodies to symbolize the mutual approaches of the German and Russian armies, though the German theme is arguably a rather silly one; at least, Béla Bartók took savage delight in satirizing it in his
Concerto for Orchestra. During the war even the more abstract-leaning Stefan Wolpe wrote a
Battle Piece (1943-7) for piano — once again marked by repeated notes.
The massive War Requiem (1961-2) by the pacifist Benjamin Britten, however — perhaps its century’s grandest anti-war musical protest, filled with snare-drum march rhythms and trumpet fanfares suspended in uneasy irony — seems to close a curved trajectory that opened with Monteverdi’s Il combattimento. Whereas musicians once thought the military mode in music could be innocently brought up with historical interest or patriotic pride, today we invoke it only to condemn it. The Vietnam War era may have rendered any non-pejorative expression of Mars verboten for the foreseeable future. In recent years the pianist Sarah Cahill commissioned anti-war pieces from many composers (Frederic Rzewski, Terry Riley, Pauline Oliveros, and Meredith Monk among them) for a project called “A Sweeter Music”; my own contribution, War Is Just a Racket, uses a 1933 text by General Smedley Butler, lamenting the army’s too-close ties to corporate interests.
Yet perhaps because Mars and Neptune were conjunct when I was born, I’ve written one un-ironic piece of battle music myself. Aside from the “Mars” movement of my own Planets (yes, I was foolhardy enough to compete with Holst, but my “Mars” is more complaining than belligerent), I depicted the battle of the Little Bighorn in my one-man electronic cantata Custer and Sitting Bull (1999), replete with sampled gunfire. The Sioux warriors are in one key, the US Cavalry in another a tritone away, and as they take turns the music jumps between two different tempos. But there’s something so peculiar about the expression of Mars in music that I have to wonder if, a couple of centuries from now, that battle scene will survive only as a curious anomaly, like Battalia a 9 or the Combat Naval or the battle of David and Goliath.
Kyle Gann is a composer who writes books about American music, including, so far; The Music of Conlon Nancarrow; American Music in the Twentieth Century; Music Downtown: Writings from the Village Voice; No Such Thing as Silence: John Cage’s 4’33”; Robert Ashley; and, coming up in 2015, a book on Ives’s Concord Sonata. His music explores tempo complexity and microtonality. He writes the blog, Postclassic and teaches at Bard College.
Oxford Music Online is the gateway offering users the ability to access and cross-search multiple music reference resources in one location. With Grove Music Online as its cornerstone, Oxford Music Online also contains The Oxford Companion to Music, The Oxford Dictionary of Music, and The Encyclopedia of Popular Music.
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World – the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only music articles the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Mars and music appeared first on OUPblog.


By: AlanaP,
on 12/5/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
richard holden,
elon,
musk,
Geography,
words,
Dictionaries,
mars,
oed,
oxford english dictionary,
place of the year,
martians,
Atlas of the World,
POTY,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Lexicography & Language,
Add a tag
By Richard Holden
The planet Mars might initially seem an odd choice for Place of the Year. It has hardly any atmosphere and is more or less geologically inactive, meaning that it has remained essentially unchanged for millions of years. 2012 isn’t much different from one million BC as far as Mars is concerned.
However, here on Earth, 2012 has been a notable year for the red planet. Although no human has (yet?) visited Mars, our robot representatives have, and for the last year or so the Curiosity rover has been beaming back intimate photographs of the planet (and itself). (It’s also been narrating its adventures on Twitter.) As a result of this, Mars has perhaps become less of an object and more of a place (one that can be explored on Google Maps, albeit without the Street View facility).
Our changing relationship with Mars over time is shown in the development of its related words. Although modern readers will probably associate the word ‘Mars’ most readily with the planet (or perhaps the chocolate bar, if your primary concerns are more earthbound), the planet itself takes its name from Mars, the Roman god of war.

Drawing of Mars from the 1810 text, “The pantheon: or Ancient history of the gods of Greece and Rome. Intended to facilitate the understanding of the classical authors, and of poets in general. For the use of schools, and young persons of both sexes” by Edward Baldwin, Esq. Image courtesy the New York Public Library.
From the name of this god we also get the word martial (relating to fighting or war), and the name of the month of March, which occurs at a time of a year at which many festivals in honour of Mars were held, probably because spring represented the beginning of the military campaign season.
Of course, nobody believes in the Roman gods anymore, so confusion between the planet and deity is limited. In the time of the Romans, the planet Mars was nothing more than a bright point in the sky (albeit one that took a curious wandering path in comparison to the fixed stars). But as observing technology improved over centuries, and Mars’s status as our nearest neighbour in the solar system became clear, speculation on its potential residents increased.
This is shown clearly in the history of the word martian. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the most common early usage of the word was as an adjective in the sense ‘of or relating to war’. (Although the very earliest use found, from Chaucer in c1395, is in a different sense to this — relating to the supposed astrological influence of the planet.)
But in the late 19th century, as observations of the surface of the planet increased in resolution, the idea of an present of formed intelligent civilization on Mars took hold, and another sense of martian came into use, denoting its (real or imagined) inhabitants. These were thought by some to be responsible for the ‘canals’ that they discerned on Mars’s surface (these later proved to be nothing more than an optical illusion). As well as (more or less) scientific speculation, Martians also became a mainstay of science fiction, the earth-invaders of H.G. Wells’s The War of the Worlds (1898) being probably the most famous example.
A century on, robotic explorers such as the Viking probes and the aforementioned Curiosity have shown Mars to be an inhospitable, arid place, unlikely to harbour any advanced alien societies. Instead, our best hope for the existence of any real Martians is in the form of microbes, evidence for which Curiosity may yet uncover.
If no such evidence of life is found, perhaps the real Martians will be future human settlers. Despite the success of Martian exploration using robots proxies, the idea of humans visiting or settling Mars is still a romantic and tempting one, despite the many difficulties this would involve. Just this year, it was reported that Elon Musk, one of the co-founders of PayPal, wishes to establish a colony of 80,000 people on the planet.
The Greek equivalent of the Roman god Mars is Ares; as such, the prefix areo- is sometimes used to form words relating to the planet. Perhaps, then, if travel to Mars becomes a reality, we’ll begin to talk about the brave areonauts making this tough and unforgiving journey.
Richard Holden is an editor of science words for the Oxford English Dictionary, and an online editor for Oxford Dictionaries.
The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) is widely regarded as the accepted authority on the English language. It is an unsurpassed guide to the meaning, history, and pronunciation of 600,000 words — past and present — from across the English-speaking world. Most UK public libraries offer free access to OED Online from your home computer using just your library card number. If you are in the US, why not give the gift of language to a loved-one this holiday season? We’re offering a 20% discount on all new gift subscriptions to the OED to all customers residing in the Americas.
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World — the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only lexicography and language articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Mars: A lexicographer’s perspective appeared first on OUPblog.


By: AlanaP,
on 12/4/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
david rothery,
mars,
planets,
VSI,
very short introduction,
place of the year,
gale,
POTY,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
rothery,
crater,
Geography,
curiosity,
Atlas of the World,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Environmental & Life Sciences,
Science & Medicine,
gale crater,
VSIs,
Add a tag

By David Rothery
So Mars is ‘Place of the Year’! It has the biggest volcano in the Solar System — Olympus Mons — amazing dust storms, and the grandest canyon of all — Valles Marineris. Mind you, the surface area of Mars is almost the same as the total area of dry land on Earth, so to declare Mars as a whole to be ‘place of the year’ seems a little vague, given that previous winners (on Earth) have been islands or single countries. If you pushed me to specify a particular place on Mars most worthy of this accolade I would have to say Gale crater, the location chosen for NASA’s Curiosity Rover which landed with great success on 6 August.
This was chosen from a shortlist of several sites offering access to layers of martian sediment that had been deposited over a long time period, and thus expected to preserve evidence of how surface conditions have changed over billions of years. Gale crater is just over 150 km in diameter, but the relatively smooth patch within the crater where a landing could be safely attempted is only about 20 km across, and no previous Mars lander has been targeted with such high precision.

Perspective view of Gale crater. Curiosity landed in the ellipse within the nearest part of the crater. Image Credit: NASA
The thing that makes Gale one of the most special of Mars’s many craters is that its centre is occupied by a 5 km high mound, nicknamed Mount Sharp, made of eroded layers of sediment. To judge from its performance so far, the nuclear powered Curiosity Rover looks well capable of traversing the crater floor and then making its way up Mount Sharp layer by layer, reading Mars’s history as it goes. The topmost layers are probably rock made from wind-blown sand and dust. The oldest layers, occurring near the base of the central mound, will be the most interesting, because they appear to contain clay minerals of a kind that can form only in standing water. If that’s true, Curiosity will be able to dabble around in material that formed in ponds and lakes at a time when Mars was wetter and warmer than today. It will probably take a year or so to pick its way carefully across ten or so km of terrain to the exposures of the oldest, clay-bearing rocks, but already Curiosity has seen layers of pebbly rock that to a geologist are a sure sign that fast-flowing rivers or storm-fed flash-floods once crossed the crater floor.

Layers at the base of Mount Sharp that Curiosity will analyze. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
The geologist in me wants to study the record of changing martian environments over time, because I like to find out what makes a planet tick. However the main reason why Mars continues to be the target for so many space missions, is that in the distant past — when those clay deposits were forming – its surface conditions could have been suitable for life to become established. Curiosity’s suite of sophisticated science instruments is designed to study rocks to determine whether they formed at a time when conditions were suitable for life. They won’t be able to prove that life existed, which will be a task for a future mission. If life ever did occur on Mars, then it might persist even today, if only in the form of simple microbes. Life probably will not be found at the surface, which today is cold, arid and exposed to ultraviolet light thanks to the thinness of its atmosphere, but within the soil or underneath rocks.
Finding life — whether still living or extinct — on another world would offer fundamental challenges to our view of our own place in the Universe. Currently we know of at least two other worlds in our Solar System where life could exist — Mars and Jupiter’s satellite Europa. It has also become clear that half the 400 billion stars in our Galaxy have their own planets. If conditions suitable for life occur on only a small fraction of those, that is still a vast number of potential habitats.
So, are we alone, or not? We don’t know how common it is for life to get started: some scientists think that it is inevitable, given the right conditions. Others regard it as an extremely rare event. If we were to find present or past life on Mars, then, provided we could rule out natural cross-contamination by local meteorites, this evidence of life starting twice in one Solar System would make it virtually unthinkable that it had not started among numerous planets of other stars too. Based on what we know today, Earth could be the only life-bearing planet in the Galaxy, but if we find independent life on Mars, then life, and probably intelligence, is surely abundant everywhere. As the visionary Arthur C. Clarke put it: “Two possibilities exist: Either we are alone in the Universe or we are not. Both are equally terrifying.” Terrifying or not, I’d like to know the answer. I don’t think Mars holds the key, but it surely holds one of the numbers of the combination-lock.
David Rothery is a Senior Lecturer in Earth Sciences at the Open University UK, where he chairs a course on planetary science and the search for life. He is the author of Planets: A Very Short Introduction. Read his previous blog post: “Is there life on Mars?”
The Very Short Introductions (VSI) series combines a small format with authoritative analysis and big ideas for hundreds of topic areas. Written by our expert authors, these books can change the way you think about the things that interest you and are the perfect introduction to subjects you previously knew nothing about. Grow your knowledge with OUPblog and the VSI series every Friday!
Oxford University Press’ annual Place of the Year, celebrating geographically interesting and inspiring places, coincides with its publication of Atlas of the World — the only atlas published annually — now in its 19th Edition. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price. Read previous blog posts in our Place of the Year series.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only geography articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Mars: A geologist’s perspective appeared first on OUPblog.


By: Alice,
on 12/3/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Geography,
mars,
atlas,
burma,
shortlist,
place of the year,
cartography,
myanmar,
longlist,
Atlas of the World,
POTY,
Social Sciences,
*Featured,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
public vote,
oxford’s atlas,
Add a tag
Since its inception in 2007, Oxford University Press’s Place of Year has provided reflections on how geography informs our lives and reflects them back to us. Adam Gopnik recently described geography as a history of places: “the history of terrains and territories, a history where plains and rivers and harbors shape the social place that sits above them or around them.” An Atlas of the World expert committee made up of authors, editors, and geography enthusiasts from around the press has made several different considerations for their choices over the years.
Warming Island was a new addition to the Atlas and conveyed how climate change is altering the very map of Earth. Kosovo’s declaration of independence not only caused lines on the map to be redrawn, but highlighted the struggle of many separatists groups around the world. In 2009 and 2010, we looked to the year ahead — as opposed to the year past — with the choices of South Africa and Yemen. Finally, last year was an easy choice as South Sudan joined us as a new country.
We took a slightly different tact with Place of the Year this year. In addition to the ideas of our Atlas committee, we decided to open the choice to the public. We created a longlist, which was open to voting, and invited additions in the comments. After a few weeks of voting, we narrowed the possible selections to a shortlist, also open to voting from the public.
Four front-runners emerged in both the longlist and shortlist: London, Syria, Burma/Myanmar, and Mars. These places have changed greatly over the years, but 2012 has been a particularly special year for each. London hosted the Queen’s Jubilee and the Summer Olympics, as well as the Libor scandal and Leveson Inquiry. The Arab Spring has spread across the Middle East and North Africa, but after the toppling of dictators in Egypt, Libya and Tunisia, civil war threatens to tear Syria apart. On the other side of the globe, the government of Burma (also known as Myanmar) is slowly moving to reform the country and only two weeks ago President Barack Obama made a historic visit to Rangoon. And finally, this August the Curiosity Rover landed on Mars. Although you can’t find Mars in our Atlas of the World (for obvious reasons), it captures the spirit of cartography: the exploration of the unknown and all that entails.
It was these four front-runners that we asked Oxford University Press employees to vote on and our Atlas committee to consider. Mars won the public vote, the OUP employee vote, and the hearts and minds of our Atlas committee.
Once we made our final decision on November 19th, we began contacting experts on Mars from around Oxford University Press to illuminate different aspects of the red planet. Inevitably, the first response we received asked us whether we had heard about the rumours surrounding NASA’s upcoming announcement. We took that as a good sign — and we’ll bring up An Atlas of Mars at our next editorial meeting.
Oxford’s Atlas of the World — the only world atlas updated annually, guaranteeing that users will find the most current geographic information — is the most authoritative resource on the market. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only geography articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.


By: AlanaP,
on 12/3/2012
Blog:
OUPblog
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
Geography,
mars,
NASA,
telescope,
curiosity,
place of the year,
hubble,
Atlas of the World,
POTY,
rover,
curiosity rover,
Place of the Year 2012,
poty 2012,
mars’,
Social Sciences,
Editor's Picks,
*Featured,
Add a tag
MARS!
It’s a city! It’s a state! It’s a country! No — it’s a planet! Breaking with tradition, Oxford University Press has selected Mars as the Place of the Year 2012.

A close-up of Mars by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Image Credit: NASA
Mars, visible in the night sky to the naked eye, has fascinated and intrigued for centuries but only in the past 50 years has space exploration allowed scientists to better understand the red planet. On 6 August 2012, NASA’s Curiosity Rover landed on Mars’ Gale Crater, and by transmitting its findings back to Earth, Curiosity has made Mars a little a less alien. Among many other accomplishments, Curiosity has swallowed Martian soil and discovered an ancient stream bed. Today, NASA is expected to make a possibly mars-shattering announcement at the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union.
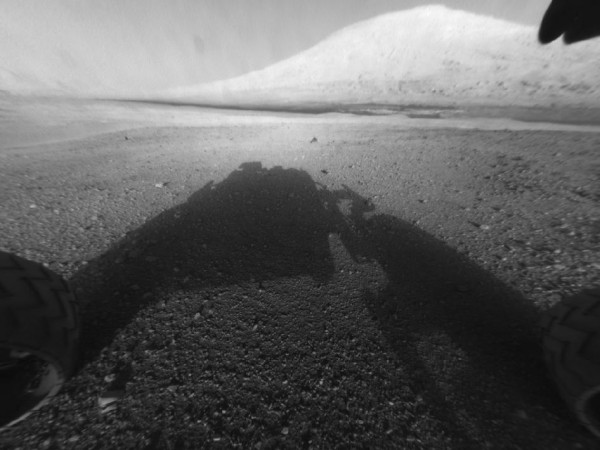

Mount Sharp, Curiosity Rover's goal. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
With an eye to the future of scientific discovery, Oxford University Press has chosen Mars in celebration of the place that has kept Earthlings excited and engaged this year. Your votes, combined with the votes of OUP employees, and the opinion of our expert Atlas of the World committee, easily led to Mars’s victory, outperforming Syria, London, Calabasas (California, USA), Greece, Istanbul, CERN, Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands, Artic Circle, and Myanmar/Burma.
Here are some of the many reasons why we’re so excited about Mars:
- While scientists have been mapping Mars from afar since the 19th century, it still represents the new and unknown — the fascination of cartographers and atlas-makers.
- Space exploration! Astrophysics! Astronomy! Geophysics! Astrobiology! There’s much to know about the universe and Earth’s place in it, and Mars is just one fascinating piece in the puzzle.
- Mars is home to the highest peak in the Solar System (Olympus Mons), but no life forms (as far as we know).
- Space exploration poses problems for traditional international diplomacy. The Outer Space Treaty is only the beginning of a complex legal framework.
- Although named after the Roman god of war, Mars acts as a muse to some of the great writers and artists, including H.G. Wells and David Bowie.
- Did Mars Curiosity steal your iPod? Curiosity wakes up to these tracks and premiered will.i.am’s Reach for the Stars by beaming the song back to earth. Even Britney Spears wants to know more.
- Mars continues to inspire new generations to study, to dream, and to stay curious.
We’ll be looking in depth at various facets of Mars on the OUPblog this week. You can check back here for the latest posts. We invite your comments and hope that you continue to stay curious!
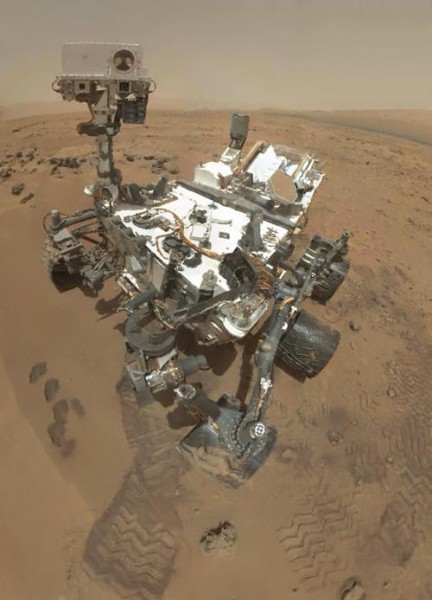

Curiosity Rover takes a self-portrait, reminding you to stay curious, OUPbloggers. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Malin Space Science Systems
Oxford’s Atlas of the World — the only world atlas updated annually, guaranteeing that users will find the most current geographic information — is the most authoritative resource on the market. The Nineteenth Edition includes new census information, dozens of city maps, gorgeous satellite images of Earth, and a geographical glossary, once again offering exceptional value at a reasonable price.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only geography articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.

In 2008, when I began submitting to publishers my children’s book on the Mars rovers Spirit and Opportunity, I got a number of rejections that basically said: We love the idea, love the writing, love the story, but we don’t think there will be interest in the market as the mission will be long over by the time the book comes out. Now, rejections are never fun to get, but these made me want to scream: This story is never over! This is the on-going story of our exploration of our solar system.
One of my beefs with the way science is often taught in school and presented in textbooks and even in many trade nonfiction children’s books is that science is portrayed as a category of facts that kids need to learn rather than an ongoing, ever-changing set of questions people have about the world around them.
That’s why I was SO pleased when my book The Mighty Mars Rovers: The incredible adventures of Spirit and Opportunitywas published as part of Houghton Mifflin’s Scientists in the Field series this June, just two months before the next Mars rover Curiosity was scheduled to land on the red planet.

There are so many connections between Spirit and Opportunity's and Curiosity’s missions that it’s nearly impossible to miss that Mars exploration is an on-going question, on-going story. Many of the same people have been involved in both missions, from the main subject of my book, Steve Squyres, the principal science investigator for Spirit and Opportunity who is also involved in the science of the new mission, to Pete Theisinger and Rob Manning, lead engineers on both missions, to Jennifer Trosper, a mission manager for both missions, and Joy Crisp, a project scientist for both missions. Watching mission control during the nail-biting landing of Curiosity was like re-living the landings of Spirit and Opportunity – the familiar faces, the tension, the worries, the hopes, the awe. (If you missed the landing, you’ve got to see this
cool 3-minute video that melds footage from mission control and launch parties across the country with simulations of the landing process.)

There’s something else in the news these days that drives home the point that space exploration and science is an on-going quest. Astronaut Neil Armstrong died on August 25, 2012. The connection? Chapter one of The Mighty Mars Rovers opens on July 20, 1969, as a thirteen-year-old boy named Steve Squyres watched in wonder as the Apollo mission put people on the moon. In 1969, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin did something (walking on the moon) that ultimately inspired a young boy to dream of sending rolling geologists to Mars. Steve Squyres and hundreds of thousands of other scientists and engineers safely landed Spirit and Opportunity on the red planet for a mission so successful that it essentially answered the question: Was there enough water on Mars to support life? (Yes!) With that question solidly answered, and with everything else we learned from Spirit and Opportunity’s mission, today, the next Mars rover Curiosity can focus on searching for other building blocks of life. THIS is science.
The Mighty Mars Rovers and many books written by my INK colleagues and others can be used to show kids that science is an on-going quest, an on-going story. With the help of the internet, readers can be guided to see the connections between a book they read on a science topic (
The Mighty Mars Rovers) and what is happening in that field today. (Check NASA's website for the latest on
Curiosity’s explorations of Mars, including other great videos.) Readers of
The Mighty Mars Rovers who follow Curiosity’s current mission can’t help but notice many parallels and connections. Teacher can also encourage readers to make these connections by asking:
- How are the missions the same?
- How are they different?
- How has rover design, launch, and landing changed?
- What are the biggest challenges of the missions?
- How were they overcome?
- What questions are the missions designed to answer?
- What tools do the rovers and scientists have to answers those questions?
- And maybe most importantly: What questions might come next?
Discussion questions like these help students experience the connection between science books and what is happening in the field right now – and inspire readers to imagine science they may want to do – questions they might want to try to answer—when they grow up.
Oh, and one more thing. All those editors who rejected my book because of timing were wrong. Not just in a philosophical sense but in a literal sense. The mission I wrote about in
The Mighty Mars Rovers is not over. Defying all expectations, Opportunity, expected to last a bit over three months in the harsh, frigid Martian environment, is
STILL roving the red planet, sending back photos and information about our neighboring planet more than
eight years later. That little rover is like the Indiana Jones of space exploration. You, your students, and your kids can catch up on
Opportunity’s most recent discoveries and see new photos sent back from Mars anytime you want.
The story continues…
Elizabeth Rusch
* A complete teachers’ guide to
The Mighty Mars Rovers, including discussion questions and hands-on activities, can be downloaded for free
here.
I have to work today so instead of an review, here's my cat and some books.
What?
:)
.jpeg?picon=3324)
By: Keith Mansfield,
on 8/6/2012
Blog:
Keith Mansfield
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
space,
Mars,
NASA,
JPL,
Publishing Industry,
Johnny Mackintosh,
Clara Mackintosh,
literary characters,
Mars Curiosity,
Gale Crater,
sheepdog on Mars,
Add a tag
In case you missed it, Johnny Mackintosh (and Clara and Bentley, and even me) only went and landed on Mars this morning: read all about it!
We’re all here, etched onto the back of the Mars Curiosity rover, in the Gale Crater:



[Update II] SUCCESS! Cyn and I watched on NASA TV last night. Gratifyingly, the cable news channels also had fairly extensive coverage.
Curiosity landed at 10:32 p.m. Aug. 5, PDT, (1:32 a.m. EDT Aug. 6) near the foot of a mountain three miles tall and 96 miles in diameter inside Gale Crater. During a nearly two-year prime mission, the rover will investigate whether the region ever offered conditions favorable for microbial life.
More
here.
[Update] Check out this great post on
How to Watch the Mars Curiosity Rover.
There's much awesomeness afoot on Mars this weekend. Tonight, in fact.
Or, early Monday morning (for those of us in the central and eastern time zones), to be exact. NASA's
Mars Curiosity rover is scheduled to set down. If you haven't heard of Curiosity, here's the deal: it's a rover about the size of a MINI Cooper that's scheduled to set down via a "sky crane." Take a look at the JPL/NASA web site
here.
Here's the NASA video on how Curiosity is going to make its descent, titled "
Seven Minutes of Terror":
.jpeg?picon=3324)
By: Keith Mansfield,
on 2/4/2012
Blog:
Keith Mansfield
(
Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags:
exoplanets,
Kepler,
ABSW,
pecha kucha,
Giovanna Tinetti,
Ofer Lahav,
dark energy,
Geraint Jones,
Peter Grindrod,
Claire Cousins,
Exomars,
Lewis Dartnell,
extremophiles,
Science,
space,
Mars,
comets,
astrophysics,
astrobiology,
Add a tag
I realize I’m privileged to have access to some of the world’s cutting edge science, but last week was particularly special with a visit to University College London to hear a mixture of astrophysicists and astrobiologists talk to journalists about their cutting edge work,organized by the ABSW, the Association of British Science Writers, of which I’m a member.
Now we all know scientists can sometimes waffle, but this brave half-dozen weren’t allowed that luxury. The format for the talks was a pecha kucha – born in Japan, you have 20 slides, each lasting for exactly 20 seconds, to get your point across. That’s 6 minutes, 40 seconds (and not a second more) to say who you are, what you do and pitch for a place in the science columns of Britain’s newspapers.
 First up, Giovanna Tinetti asked what exoplanets are actually made of. For those out of the loop, exoplanets are those orbiting other stars, far beyond out own solar system. We weren’t sure such things even existed until the 1990s, but nowadays there are more than 700 confirmed cases, with hundreds more candidates awaiting confirmation. recently some astronomers have gone so far as to sayy that every star in our galaxy must have planets orbiting.The most productive way to search for these faraway worlds is by using the Kepler Space Telescope. Looking back along a populous spiral arm of the Milky Way, this other Hubble is a study in concentration, staring fixedly at a single window on the stars, watching for the most minute variation in their light. And by analying this light – the chemical clues hidden within the spectra, scientists like Giovanna can tell what planets hundreds of light years away are made from. She’s looking for those that are habitable. Soon, New Earth need not be a thing of science fiction stories, especially if Giovanna’s plans for ECHO, the Exoplanet Characterisation Observatory, are approved by ESA (the European Space Agency).
First up, Giovanna Tinetti asked what exoplanets are actually made of. For those out of the loop, exoplanets are those orbiting other stars, far beyond out own solar system. We weren’t sure such things even existed until the 1990s, but nowadays there are more than 700 confirmed cases, with hundreds more candidates awaiting confirmation. recently some astronomers have gone so far as to sayy that every star in our galaxy must have planets orbiting.The most productive way to search for these faraway worlds is by using the Kepler Space Telescope. Looking back along a populous spiral arm of the Milky Way, this other Hubble is a study in concentration, staring fixedly at a single window on the stars, watching for the most minute variation in their light. And by analying this light – the chemical clues hidden within the spectra, scientists like Giovanna can tell what planets hundreds of light years away are made from. She’s looking for those that are habitable. Soon, New Earth need not be a thing of science fiction stories, especially if Giovanna’s plans for ECHO, the Exoplanet Characterisation Observatory, are approved by ESA (the European Space Agency).
 Ofer Lahav, Professor of Astronomy at UCL, chose to talk about dark energy, the mysterious entity that apparently makes up three quarters of out universe, but which we didn’t even know was there until 1998. For me the most incredible, unexpected discovery of the last fifty years has been that the rate of expansion of the universe is increasing. No one expected this. Everyone wants to know why, but Ofer was impressively agnostic in his views. Either an entity we call dark energy permeates space itself, acting as Einsteins cosmological constant, or the best theories we have are very wrong. Once upon a time our best theory was Newton’s, but it couldn’t explain why Mercury orbited the Sun the way it did. Along came Einstein, General Relativity and a revolution in science. With the dark energy anomaly, are we on the cusp of another such paradigm shift?
Ofer Lahav, Professor of Astronomy at UCL, chose to talk about dark energy, the mysterious entity that apparently makes up three quarters of out universe, but which we didn’t even know was there until 1998. For me the most incredible, unexpected discovery of the last fifty years has been that the rate of expansion of the universe is increasing. No one expected this. Everyone wants to know why, but Ofer was impressively agnostic in his views. Either an entity we call dark energy permeates space itself, acting as Einsteins cosmological constant, or the best theories we have are very wrong. Once upon a time our best theory was Newton’s, but it couldn’t explain why Mercury orbited the Sun the way it did. Along came Einstein, General Relativity and a revolution in science. With the dark energy anomaly, are we on the cusp of another such paradigm shift?
View Next 5 Posts



 So yesterday I started composing in my head what I wanted to say about Andy Weir’s
So yesterday I started composing in my head what I wanted to say about Andy Weir’s 





 Anatoly Liberman is the author of
Anatoly Liberman is the author of 

 Although there had been interest in Mars earlier, towards the end of the nineteenth century there was a sudden surge of novels describing travel to the red planet. One of the earliest was Percy Greg’s Across the Zodiac (1880) which set the pattern for early Mars fiction by framing its story as a manuscript found in a battered metal container. Greg obviously assumed that his readers would find the story incredible and sets up the discovery of the ‘record’, as he calls it, by a traveler to the USA to distance himself from the extraordinary events within the novel. The space traveler is an amateur scientist who has stumbled across a force in Nature he calls ‘apergy’ which conveniently makes it possible for him to travel to Mars in his spaceship. When he arrives there, he discovers that the planet is inhabited. Since then, the conviction that beings like ourselves live on Mars has constantly fed writings about the planet. The American astronomer
Although there had been interest in Mars earlier, towards the end of the nineteenth century there was a sudden surge of novels describing travel to the red planet. One of the earliest was Percy Greg’s Across the Zodiac (1880) which set the pattern for early Mars fiction by framing its story as a manuscript found in a battered metal container. Greg obviously assumed that his readers would find the story incredible and sets up the discovery of the ‘record’, as he calls it, by a traveler to the USA to distance himself from the extraordinary events within the novel. The space traveler is an amateur scientist who has stumbled across a force in Nature he calls ‘apergy’ which conveniently makes it possible for him to travel to Mars in his spaceship. When he arrives there, he discovers that the planet is inhabited. Since then, the conviction that beings like ourselves live on Mars has constantly fed writings about the planet. The American astronomer 















 First up,
First up,  Ofer Lahav
Ofer Lahav
omg the baby meows are sooooo cute!
He is so sweet. Thank you for sharing with us. It made my day :)
He is SO cute! Thanks for the smile - I needed that. :)