Viewing: Blog Posts Tagged with: children’s literature about space exploration, Most Recent at Top [Help]
Results 1 - 3 of 3
Blog: WOW! Women on Writing Blog (The Muffin) (Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags: imagination, love, joy, emotions, ocean, sexy, smell, taste, lemons, feel, imagery, writing description, see, spray, man on beach, evokes, provoke, Add a tag
Blog: OUPblog (Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags: Philosophy, experimental, A-Featured, A-Editor's Picks, universe, questions, Aristotle, experimental philosophy, feel, Hume, Knobe, Netzche, Nichols, think, morally, philosophers, logical, inevitable, responsible, Add a tag
Experimental philosophy is a new movement that seeks to return the discipline of philosophy to
a focus on questions about how people actually think and feel. In Experimental Philosophy we get a thorough introduction to the major themes of work in experimental philosophy and theoretical significance of this new research. Editors Joshua Knobe and Shaun Nichols have been kind enough to explain this all in simple terms below. Joshua Knobe is an assistant professor in the philosophy department at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Shaun Nichols is in the Philosophy Department and Cognitive Science Program at the University of Arizona. He also is the author of Sentimental Rules and co-author (with Stephen Stich) of Mindreading. Be sure to check out their Myspace page and their blog.
The reason the two of us first started doing philosophy is that we were interested in questions about the human condition. Back when we were undergraduates, we were captivated by the ideas we found in the work of philosophers like Nietzsche, Aristotle, and Hume. We wanted to follow in their tracks and think and write about human beings, their thoughts and feelings, the way they get along with each other, the nature of the mind.
Then we went to graduate school. What we found there was that the discipline of philosophy was no longer focused on questions about what human beings were really like. Instead, the focus was on a very technical, formal sort of philosophizing that was quite far removed from anything that got us interested in philosophy in the first place. This left us feeling disaffected, and a number of researchers at various other institutions felt the same way.
Together, several of these researchers developed the new field of experimental philosophy. The basic idea behind experimental philosophy is that we can make progress on the questions that interested us in the first place by looking closely at the way human beings actually understand their world. In pursuit of this objective, practitioners of this new approach go out and conduct systematic experimental studies of human cognition.
For example, in the traditional problem of free will, many philosophers have maintained that no one can be morally responsible if everything that happens is an inevitable consequence of what happened before. But the entire debate is conducted in a cold, logical manner. Experimental philosophers thought that maybe the way people actually think about these issues isn’t always so cold and logical. So first they tried posing the question of free will to ordinary people in a cold abstract manner. After describing a universe in which everything is inevitable, they asked participants, “In this Universe is it possible for a person to be fully morally responsible for their actions?” When the question was posed in this way, most people responded in line with those philosophers who claimed that no one can be responsible if everything is inevitable. But the experimentalists also wanted to see what would happen if people were given cases that got people more emotionally involved in the situation. So they once again described a universe in which everything that happens is inevitable, and then they asked a question that was sure to arouse strong emotions. It concerned a particular person in that Universe, Bill: “As he has done many times in the past, Bill stalks and rapes a stranger. Is it possible that Bill is fully morally responsible for raping the stranger?” Here the results were quite different. People tended to say that Bill was in fact morally responsible. So which reaction should we trust, the cold logical one or the emotionally involved one? This is the kind of question that experimental philosophy forces on us.
But that’s just one example. If you want to learn about more of the experimental studies that have been done, you can take a look at the recent articles on experimental philosophy in the New York Times and Slate.
Blog: I.N.K.: Interesting Non fiction for Kids (Login to Add to MyJacketFlap)
JacketFlap tags: NASA missions, children’s literature about space exploration, children’s literature, Mars, Loreen Leedy, space exploration, science, Mars, Add a tag
In a decade or two people may set foot on Mars, though there are many technical obstacles to solve first. Actually the title is a trick question, because humans have already been to the Red Planet many times with the help of orbiters, landers, and robotic rovers. My husband Andrew Schuerger and I were inspired to create Messages From Mars by the many scientific discoveries and fantastic photographs taken in the past few years. We sent an international group of kids and a hoverbot on their way… to make their trip quicker and easier, the book is set a hundred years in the future. To see a live preview of the entire book, click on the cover below:
To see a larger version, click on the orange eyeballs.
Note to authors: For info about how to embed book previews in a blog or web site, please see the end of this post.
There was so much great information we wanted to include that the book kept getting longer and more detailed. After a few debates with the publisher, we finally came to a compromise—instead of the usual 32 pages in most picture books, it has 40 pages. For reviews, Mars trivia, and activities, please see my web site.
The lucky students who have won a trip to Mars learn many amazing facts about the planet on the way. For example, it has the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons. They touch down to visit the historic sites of the Viking, Pathfinder, and the Spirit/Opportunity missions. Along the way they send emails home to share what they’re seeing. Readers who are familiar with my Postcards From Pluto: A Tour of the Solar System may recall its similar approach.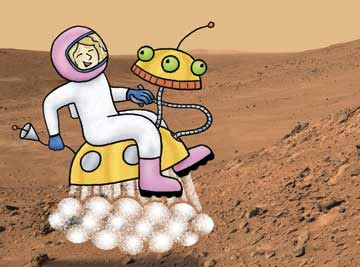
As you can see, the artwork consists of real photographs taken on the surface of Mars, with the characters drawn on top. Andy searched through many NASA, JPL, and ESA (European Space Agency) web sites to find great images to use as settings. There's a list of those web sites at the end of the book. One site that is not listed in the book gives updates about the still-working Spirit and Opportunity rovers. Another fun one is Rock Around the World, which invites kids to mail in rocks to be analyzed using a tool similar to one on the rovers. How cool is that?
By the way, the photographs we used have already been paid for by all of us (the tax-payers, that is) and are generally free for use with proper credit, as detailed in the NASA/JPL image use policy.
Not incidentally, Andy is a scientist who does quite a bit of Mars-related research in his Mars simulation chamber. The chamber is like having a little piece of the Red Planet right inside his lab, which is located at the Kennedy Space Center. In creating this book, it naturally helped tremendously that he is so familiar with the material and knows what he is looking at in the photographs. We ran across several mislabeled images in other books, such as a photograph of Venus mistakenly included in a book about Mars.
An obvious yet often overlooked point is that the facts in nonfiction books should be carefully checked and double-checked. Mistakes can happen in a number of ways… photographs can be difficult to interpret… it’s easy to assume too much… and writers often introduce subtle (or big) mistakes when rewording something. Beware of relying too heavily only on other published books or the Internet. Some sites are very reliable, of course, such as NASA’s. Unless one is very well-informed about a topic, it’s a good idea to enlist an expert to look the project over, if at all possible. Many specialists are happy to help because they want accurate info in circulation about their favorite subject. We showed Messages From Mars to two space scientists to ensure no glitches had crept in.
Speaking of the 4th rock from the sun, did you know another lander is on its way to Mars right now? The Phoenix is scheduled to land in about three months from now, on May 25, 2008. Its mission is to study the soil and ice near the north polar ice cap to find out if the area was ever hospitable to life. While not a rover, it has a built-in camera and weather station as well as microscopes, a gas analyzer and a digging arm to go down as far as one meter. For the latest news on its progress, check here.
Photo credit: Andrew Schuerger
Andy played a part in making the Phoenix photographs as accurate as possible. When it lands, Phoenix will take a picture of special colored “targets” that were photographed on Earth prior to launch. This will allow scientists to match the targets and thus get accurate colors in the Martian landscape images. But the targets need a special treatment to artificially age them before they go to Mars, because its harsh UV environment would change their color. So Andy placed the targets in his simulation chamber and zapped them to stabilize their color. Soon, the targets will be on the surface of Mars! If only we could go, too…
Note to authors: How to embed a “minibook”
Any picture book available on the Lookybook site may be put on a web site or blog by anyone, not just its author and/or illustrator. Assuming a book is available (if not, ask your publisher about it), search by title or author and go to the book’s page. There will be a row of buttons under it, including Embed this Book. Doubleclick on the button, copy the code, then in Blogger’s Posting window click on Edit Html and paste the code into your post. That's it! (You have to go to Preview mode to actually see anything, it won't show in Compose mode.) A similar process should work with the various web site and blog programs. What will appear on your blog or web site is a minibook—the larger version can be viewed on the Lookybook site. I have no association with them, just love the idea that readers can see my backlist titles, even if a bookstore doesn't have a copy available for them to page through.




My mouth puckers every time I look at those lemons.
A lot of people read this and I got some really great comments on facebook about it, but they can't leave a comment on here. Some ladies want to be on that beach. Also I got a variety of answers on what comes to mind when certain words are said.