 In this post, Tu Books Publisher Stacy Whitman discusses why avoiding discussions of race with young people can do more harm than good.
In this post, Tu Books Publisher Stacy Whitman discusses why avoiding discussions of race with young people can do more harm than good.
Many African American parents already know what “the talk” is. It’s not the talk that many white parents might expect—we’re not talking about the birds and the bees. No, this “talk” is the one where black parents have to sit with their children and discuss how they might be perceived by the world around them: particularly police, but also teachers, neighbors, and friends who are not from their racial background.
Though the burden often falls on parents of color alone to discuss these issues with their children, in reality all parents should address race with their kids in a conscious and meaningful way. Communities are also seeking ways to address interpersonal racial issues,  particularly in schools. Having the tools to know how to discuss racial matters is essential for children from all backgrounds.
particularly in schools. Having the tools to know how to discuss racial matters is essential for children from all backgrounds.
Research has shown that the “colorblind” approach—teaching children that it is racist to acknowledge racial and ethnic differences—is doing no one any favors, and in fact can reinforce racist attitudes and assumptions, and especially reify systemic racism. “Black children know irrefutably that they’re black by the time they’re about 6 years old and probably earlier,” one article noted in our research. Do white children know they’re white? If not, how do they think of themselves?
At Lee & Low, we’ve always believed that even the youngest readers have the capacity to understand and appreciate difference—that’s why many of our children’s books address issues like racism and discrimination. But you don’t have to take our word for it: many experts, educators, and academics have done work on this topic as well and their recommendations can help point parents and teachers in the right direction.
“Young children are hard-wired in their brains to notice difference and to categorize it. So it is vital during early childhood to put some context around making sense of differences,” said Shannon Nagy, preschool director in 2011 at Lincoln Park Cooperative Nursery School in Chicago.
Studies have also shown that not addressing difference does not make children colorblind—it only encourages them to absorb the implicit racial messages of American society. Children learn that race is a category even when parents try to teach them not to recognize race. Much like children learn to perform regional accents even when their parents are from another location, children learn  how the larger society around them views race, via inference and transductive reasoning. “In other words, children pick upon the ways in which whiteness is normalized and privileged in U.S. society.”
how the larger society around them views race, via inference and transductive reasoning. “In other words, children pick upon the ways in which whiteness is normalized and privileged in U.S. society.”
Teaching children to be “colorblind” has led children (and adults) to believe that it’s rude or racist to even point out racial differences—even kids of color. This makes it exponentially harder to have frank discussions about racial issues when they need to be had.
“Nonwhite parents are about three times more likely to discuss race than white parents,” said a 2007 study. “It’s the children whose parents do directly address race — and directly means far more than vaguely declaring everyone to be equal — who are less likely to make assumptions about people based on the color of our skin.”
One study even had white parents dropping out of the project when the researchers asked them to discuss racial attitudes with their children, even when they went into the study knowing that it was intended to measure children’s racial attitudes.
Many argue that “the talk” should happen far more often than once, and that parents shouldn’t bear the sole burden to teach their kids about race—that it is a community-wide issue.
Erin Winkler provides several ways for parents and teachers to address the biases that children might pick up, including discussing  the issue in an age-appropriate way, with accurate information that doesn’t shame or silence children for having questions. They also suggest encouraging complex thinking and taking children’s questions and biased statements seriously—“When children are taught to pay attention to multiple attributes of a person at once (e.g., not just race), reduced levels of bias are shown,” the author notes, and suggests that the most important thing parents and teachers can do is to give children information that empowers them to be anti-racist.
the issue in an age-appropriate way, with accurate information that doesn’t shame or silence children for having questions. They also suggest encouraging complex thinking and taking children’s questions and biased statements seriously—“When children are taught to pay attention to multiple attributes of a person at once (e.g., not just race), reduced levels of bias are shown,” the author notes, and suggests that the most important thing parents and teachers can do is to give children information that empowers them to be anti-racist.
One New York City-area school asked, “Can racism be stopped in the third grade?” They began a “racial affinity program,” in which elementary-age kids were sorted by racial groups for discussions of questions that “might seem impolite otherwise,” and to then come together as a school community to discuss these questions and experiences in a way that fosters greater communication. Parents and students are mixed on whether this program succeeded, with Asian students noting that the discussions of race still focused on the dichotomy of black and white, and some parents uncomfortable with the idea of discussing race at all. The administration notes, however, that many of their students of color needed this program—mandatory for all students—to combat microaggressions between students.
Allie Jane Bruce, the librarian at Bank Street School in New York City, has been discussing race, biases, and stereotypes with the students in her school for three years, using children’s book covers as a launching point. “I’m constantly delighted by the new discoveries kids make, and by the wisdom and insight already present in 11- and 12-year-olds,” Bruce noted in her most recent series of blog posts about the curriculum, which she has named “Loudness in the Library.” She notes especially that kids at this age tend to feel very uncomfortable with discussing race at first. “The fact that race-related conversations are so very fraught is a huge part of the problem. We must be able to communicate in order to solve problems that exist at interpersonal, institutional, and societal levels. If kids in 6th grade already have the inclination to stay silent in conversations on race, how much stronger will that inclination be in adults? And if we can’t talk about race and racism, how will things ever get better?”
Parents, what does “the talk” look like in your home? Teachers and librarians, how do you approach discussions about race with your students and patrons?
 Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.
Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.
The following is a note from our Publisher, Jason Low, published in this month’s e-newsletter:
 It’s been a hard few weeks for those of us following the news out of Ferguson, Missouri. While the exact details of Michael Brown’s death remain unknown, we can already see how this latest incident fits into a larger narrative in this country in which people of color are routinely discriminated against and subject to violence based on the color of their skin. Healing and change cannot begin until we as a country acknowledge the role racism plays not just in events like Michael Brown’s death, but in the everyday lived experiences of the 37% of America that is not white.
It’s been a hard few weeks for those of us following the news out of Ferguson, Missouri. While the exact details of Michael Brown’s death remain unknown, we can already see how this latest incident fits into a larger narrative in this country in which people of color are routinely discriminated against and subject to violence based on the color of their skin. Healing and change cannot begin until we as a country acknowledge the role racism plays not just in events like Michael Brown’s death, but in the everyday lived experiences of the 37% of America that is not white.
From a distance, it can seem like our book-filled corner of the world doesn’t have much to do with Michael Brown’s death, but we know better. The need for more diverse books and better representation is urgent. Poor representation doesn’t just damage self-esteem and confidence of children of color, it also perpetuates a skewed version of society as a whole. How can true equality ever exist if we are literally not even on the same page? Promoting diverse books is about creating a safer space for all children.
There are no easy ways to teach children about what’s happening in Ferguson, but here are couple links we’ve come across that help illuminate the issues and, perhaps, let us find teachable moments:
The Murder of Sean Bell: From Pain to Poetry
What did you tell your kids after the Zimmerman Verdict?
5 Books to Instill Confidence in African American Children
A Dream Conferred: Seven Ways to Explore Race in the Classroom
10 Resources for Teaching About Racism
America’s Racial Divide, Charted
The Case for Reparations
Stark Racial Divisions in Reactions to Ferguson Police Shooting
We’ll add more links as we find them; meanwhile, please do share your favorites in the comments.
Filed under:
Dear Readers,
Diversity, Race, and Representation,
Educator Resources Tagged:
Ferguson,
race,
Race issues,
racism,
teaching about race 

It’s no secret that here at Lee & Low Books we value diversity – it is literally why we are in business. But we don’t always get down to the basics. Sharing the low numbers of books by/about people of color is not the same as convincing people we need more of them. Just dip your toes into the comments section of any major article about diversity in children’s books and you’ll see what I’m talking about.
When you don’t convince people that the lack of diversity matters, what you get is more of the same. And in publishing, more of the same pretty much looks like this: BookCon, a major one-day event for readers in New York City, releases a lineup of 31 participating authors…and all of them are white.
BookCon is the latest example and certainly a frustrating one, but it is by no means an isolated incident. It’s heartening to see so many recent articles covering the lack of diversity in children’s books, but the question is how that discussion can be turned into action on a large scale to change things. The status quo – massive underrepresentation of people of color – is like a huge, heavy boulder that needs to be moved. Awareness alone will not move it an inch. What’s required is a lot of people to give it a push.
That’s why I love the new #WeNeedDiverseBooks campaign happening this week. Here’s your chance to share with the world why diversity in books matters to you and why you want more of it:

Now is the time to raise our voices into a roar that can’t be ignored. Here’s how:
On May 1st at 1pm (EST), there will be a public call for action that will spread over 3 days. We’re starting with a visual social media campaign using the hashtag #WeNeedDiverseBooks. We want people to tweet, Tumblr, Instagram, Facebook, blog, and post anywhere they can to help make the hashtag go viral.
For the visual part of the campaign:
- Take a photo holding a sign that says “We need diverse books because ___________________________.” Fill in the blank with an important, poignant, funny, and/or personal reason why this campaign is important to you.
- The photo can be of you or a friend or anyone who wants to support diversity in kids’ lit. It can be a photo of the sign without you if you would prefer not to be in a picture. Be as creative as you want! Pose the sign with your favorite stuffed animal or at your favorite library. Get a bunch of friends to hold a bunch of signs.
- However you want to do it, we want to share it! There will be a Tumblr at http://weneeddiversebooks.tumblr.com/ that will host all of the photos and messages for the campaign. Please submit your visual component by May 1st to [email protected] with the subject line “photo” or submit it right on our Tumblr page here and it will be posted throughout the first day.
- Starting at 1:00PM (EST) the Tumblr will start posting and it will be your job to reblog, tweet, Facebook, or share wherever you think will help get the word out.
- The intent is that from 1pm EST to 3pm EST, there will be a nonstop hashtag party to spread the word. We hope that we’ll get enough people to participate to make the hashtag trend and grab the notice of more media outlets.
- The Tumblr will continue to be active throughout the length of the campaign, and for however long we need to keep this discussion going, so we welcome everyone to keep emailing or sending in submissions even after May 1st.
On May 2nd, the second part of our campaign will roll out with a Twitter chat scheduled for 2pm (EST) using the same hashtag. Please use #WeNeedDiverseBooks at 2pm on May 2nd and share your thoughts on the issues with diversity in literature and why diversity matters to you.
On May 3rd, 2pm (EST), the third portion of our campaign will begin. There will be a Diversify Your Shelves initiative to encourage people to put their money where their mouth is and buy diverse books and take photos of them. Diversify Your Shelves is all about actively seeking out diverse literature in bookstores and libraries, and there will be some fantastic giveaways for people who participate in the campaign! More details to come!
We hope that you will take part in this in any way you can. We need to spread the word far and wide so that it will trend on Twitter. So that media outlets will pick it up as a news item. So that the organizers of BEA and every big conference and festival out there gets the message that diversity is important to everyone. We hope you will help us by being a part of this movement.
We’re excited to participate in this campaign and hope you will too, beginning with this question:
Why do you need diverse books?
Filed under:
Publishing 101,
The Diversity Gap Tagged:
diversity,
diversity gap,
teaching about race,
weneeddiversebooks 

 Jill Eisenberg, our Resident Literacy Expert, began her career teaching English as a Foreign Language to second through sixth graders in Yilan, Taiwan as a Fulbright Fellow. She went on to become a literacy teacher for third grade in San Jose, CA as a Teach for America corps member. She is certified in Project Glad instruction to promote English language acquisition and academic achievement. In her column she offers teaching and literacy tips for educators.
Jill Eisenberg, our Resident Literacy Expert, began her career teaching English as a Foreign Language to second through sixth graders in Yilan, Taiwan as a Fulbright Fellow. She went on to become a literacy teacher for third grade in San Jose, CA as a Teach for America corps member. She is certified in Project Glad instruction to promote English language acquisition and academic achievement. In her column she offers teaching and literacy tips for educators.
Infographics’ format and economy of words make infographics engaging and accessible to children, reluctant readers, visual learners, and English Language Learners. As infographics contain multiple layers of information, they are a challenging medium for students to practice inferences and interpretation. Lee & Low Books’ infographic series on the diversity gap in major spheres of influence is a valuable vehicle to build students’ visual literacy skills and understanding of diversity. The following discussion questions and suggested activities were created based on the Diversity Gap in the Academy Awards infographic, but these can be applied to the rest of the series.
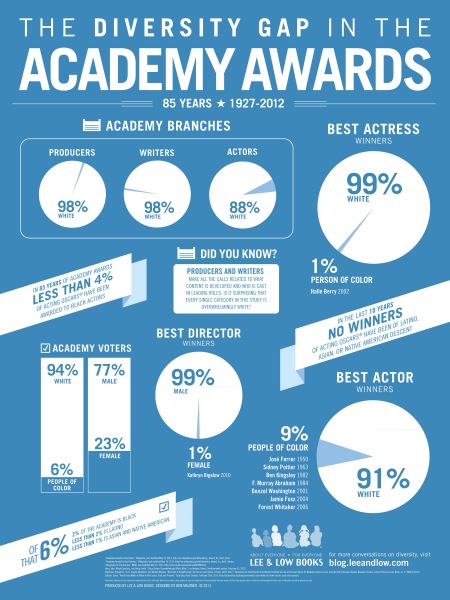
Infographic: The Diversity Gap in the Academy Awards (click to enlarge)
Discussion questions to consider with your students:
- What patterns do you see? What trends do you see? How are the different charts related?
- What is the central idea of this infographic? How do the words, phrases, and visuals interact to affirm the central idea?
- Based on the infographic, what does “diversity gap” mean in terms of the Academy Awards?
- What might the author’s purpose be in choosing this medium to convey the central idea (to shame, inspire, shock, etc.)?
- Does the infographic make the central idea clear and obvious? How does the infographic use an economy of words, language, typography, pie charts, bar graphs, negative space, and title to communicate the central idea?
- What type of infographic is this (flow chart, web, map, graph, diagram, table, timeline)? What might the author’s purpose be in choosing this type of infographic? How effective is this format of infographic at organizing and displaying data compared to just text?
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the infographic as a form of communication as compared to text alone. Is this the most effective and convincing way to convey information about a lack of diversity at the Academy Awards? Why or why not?
- Why might the creators have assembled this information about the Academy Awards and race at all?
- Who is the intended audience (moviegoers, actors, directors, writers, producers, movie studios, general public, government officials)? What might the creators of this infographic want them to do with this information?
- What is the context of this infographic? What major events in the United States were taking place when this infographic was created? Why is it important to understand the context of the infographic?
- Is this infographic’s argument and presentation persuasive or compelling? Why or why not? Analyze this infographic’s effectiveness in inspiring activism.
- Based on the information presented, what can you predict future trends will be for award winners, actors, directors, producers, and writers?
- Can you determine causes for the lack of diversity in this infographic? Why or why not? How might researchers go about figuring out the cause(s) for the historical and current lack of diversity in the Academy Awards?
- What is the impact of a lack of diversity amongst writers, actors, producers, directors, and award winners? What does it mean to be a young child growing up and consuming this form of media (movies)? What will they see? What will they not see? Tell me more about the possible effects of this situation and current trends.
Suggested activities:
- Challenge students to translate this infographic’s central idea into a written argument. Students should use key details and evidence from the infographic to assert the central idea.
- Have students revise or add on to make the infographic more effective. Students should consider format, adding or deleting information, and more. What would make the infographic stronger, more persuasive, or more memorable?
- Encourage students to investigate how these percentages compare to the general public. Students can use the United States Census data for demographics.
- Have students investigate possible causes for the lack of diversity in the Academy Awards. Urge students to propose ways to change these trends.
- If possible, ask students to research the percent of moviegoers who are people of color. Check industry publications or major news periodicals. How do these numbers compare to the information in the infographic?
- Permit students to interview their grade, class, or school on questions, including: Do you go to the movies? How often? What kinds of movies do you see? Who are your favorite actor and actress in Hollywood today? Who is a director/actor/actress of color that you have seen in a movie recently? Why do you think there aren’t more movies by and with people of color? Students can organize and display data in graphs and present findings to the class. Reflect on this information’s relationship to the infographic’s central idea.
- Dig deeper—investigate the artists that were nominated each year. How many were people of color over those 85 years? What roles did these artists play in the movies they were nominated for? What genres of movies were they in for this nomination? Explore the people of color who did win best actress or best actor. What roles did they play and what kind of movies were they in when they won for best acting?
- Compare this to other Lee & Low Books’ infographics in the series: The Tony Awards, The Emmy Awards, Children’s Book Publishing, The NY Times Top 10 Bestsellers List, and American Politics. Consider central idea, evidence, format, and audience.
- Update the information to include the 2013 and 2014 Academy Awards results. What changed? What did not change?
For further reading on teaching visual literacy and diversity in the classroom, check out these fantastic resources:
How are you building visual literacy skills in the classroom? Let us know below!
Filed under:
Curriculum Corner Tagged:
Academy Awards,
CCSS,
common core standards,
diversity,
Educators,
ELA common core standards,
History,
infographics,
Oscars,
Race issues,
reading comprehension,
teaching about race,
visual literacy 

 In this post, Tu Books Publisher Stacy Whitman discusses why avoiding discussions of race with young people can do more harm than good.
In this post, Tu Books Publisher Stacy Whitman discusses why avoiding discussions of race with young people can do more harm than good. particularly in schools. Having the tools to know how to discuss racial matters is essential for children from all backgrounds.
particularly in schools. Having the tools to know how to discuss racial matters is essential for children from all backgrounds.  how the larger society around them views race, via inference and transductive reasoning. “In other words, children pick upon the ways in which whiteness is normalized and privileged in U.S. society.”
how the larger society around them views race, via inference and transductive reasoning. “In other words, children pick upon the ways in which whiteness is normalized and privileged in U.S. society.” the issue in an age-appropriate way, with accurate information that doesn’t shame or silence children for having questions. They also suggest encouraging complex thinking and taking children’s questions and biased statements seriously—“When children are taught to pay attention to multiple attributes of a person at once (e.g., not just race), reduced levels of bias are shown,” the author notes, and suggests that the most important thing parents and teachers can do is to give children information that empowers them to be anti-racist.
the issue in an age-appropriate way, with accurate information that doesn’t shame or silence children for having questions. They also suggest encouraging complex thinking and taking children’s questions and biased statements seriously—“When children are taught to pay attention to multiple attributes of a person at once (e.g., not just race), reduced levels of bias are shown,” the author notes, and suggests that the most important thing parents and teachers can do is to give children information that empowers them to be anti-racist. Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.
Stacy Whitman is Editorial Director and Publisher of Tu Books, an imprint of LEE & LOW BOOKS that publishes diverse science fiction and fantasy for middle grade and young adult readers.






Thanks so much, Stacy, for this wonderful and useful gathering of ideas and resources about why and how to talk about race with children. When we don’t, what children pick up about race – and neuroscientists are discovering that children notice racial differences at least by the age of 6 months – is the silence. They learn that though they see race, adults don’t want them to talk about it.
Of course the challenge for many white parents and teachers is that, having rarely talked about race ourselves, it can be awkward and uncomfortable to do so with children. Diverse books are such a great way to introduce the topic. Sharing books with children, we can give them both permission and language to say what they see. You can start with the entire catalog of Lee & Low books, and here’s a list with some thoughts on types of books: http://coloringbetween.blogspot.com/2011/10/how-to-talk-about-race-list-of-books.html
Another argument for diverse books is that they can actually reduce the intergroup anxiety which leads to prejudice. Here’s a report on how picture books about friends from different racial groups can shift children’s attitudes: http://www.slj.com/2014/05/diversity/how-cross-racial-scenes-in-picture-books-build-acceptance/
And here are a few other resources I’ve found particularly useful:
– THE FIRST R: HOW CHILDREN LEARN RACE & RACISM, by Debra Van Ausdale and Joe Feagin, is a fascinating study of racial attitudes in 3-5-year-old children in a diverse preschool.
– ARE WE BORN RACIST? New Insights from Neuroscience and Positive Psychology, edited by Jason Marsh, Rodolfo Mendoza-Denton, & Jeremy Adam Smith, is a highly accessible collection of short essays about the latest findings on race. Great for a book group discussion.