The date-line is 2014. An outbreak of a deadly disease in a remote region, beyond the borders of a complacent Europe. Local deaths multiply. The risk does not end with death, either, because corpses hold the highest risk of contamination and you must work to contain their threat. All this is barely even reported at first, until the health of a Western visitor, a professional man, breaks down.
The post Why bother reading Bram Stoker’s Dracula? appeared first on OUPblog.
 Spillover: Animal Infections and the Next Human Pandemic David Quammen
Spillover: Animal Infections and the Next Human Pandemic David Quammen
We’re all going to die. And it’s probably bats or monkeys that will do us in.
As you may remember, I’m a huge fan for medical epidemic books and stories so I was very excited to come across this one, which is about diseases we get from animals, and the science of how a spillover works-- what makes something go from an animal to a human and then make large numbers of us very sick?
Quammen looks at several zoonosis (infections we get from animals) throughout history, and the history of how it made people sick, how they figured out what was going on, and what made it spillover and spread. And he looks at A LOT of diseases such as Hendra, Ebola, SARS, AIDS, Malaria, Lyme, and a host of others. Along the way, he also talks to many scientists about what they’re doing now to be ready for the next one-- what will it be, where will it hit, what can we do to be prepared.
One on hand it’s fascinating. On the other, it’s terrifying (even though he doesn’t want us to freak out too much. I mean, we will all die at some point. And probably not of the next BIG ONE. Which will probably be a flu. And probably from bats or monkeys. Man, I really like bats.)
It’s very interesting, but it does occasionally get bogged down (I found the AIDS stuff a little too academic and wasn’t a fan of his speculative fiction about how it spread in humans).
It was a weird one, because I LOVED it, but it took me FOREVER to finish. Not sure why.
If you liked Outbreak and The Hot Zone, you should probably read this one (if nothing else, just to find out that everything you thought you knew about Ebola is false.) Plus! It's an Outstanding Book for the College Bound.
Book Provided by... my local library
Links to Amazon are an affiliate link. You can help support Biblio File by purchasing any item (not just the one linked to!) through these links. Read my full disclosure statement.
By Peter C. Doherty
A recent New York Times editorial by author David Quammen highlighted the seriousness of the current Ebola outbreak in Guinea, but made the point that there is no great risk of any global pandemic. That’s been generally true of the viruses that, like Ebola, cause exudative diathesis, or bleeding into the tissues, and present with horrific symptoms. There’s a whole range of such infections caused by a spectrum of different virus types. These pathogens are generally maintained asymptomatically in wildlife “reservoir” species, including fruit and insectivorous bats, monkeys, field mice, and various other rodent species. Breathing dust contaminated with dried mouse feces can lead, for example, to infection with the Sin Nombre hantavirus that caused a recent outbreak in Yellowstone National Park. Others (like Ebola) may “jump” across to us from bats and are then transmitted between people following contact with contaminated human blood and other secretions.
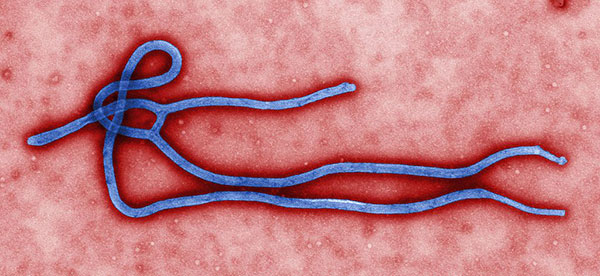
Ebola virus virion.
From the pandemic aspect, the most dangerous we’ve seen to date is the SARS coronavirus that, in 2002, came out of nowhere to kill some 800 people in the Asia/Pacific region and also caused cases in Toronto. Spread via the respiratory route or by hand-to-face transmission following contact with contaminated surfaces this virus would, if it had emerged prior to the 19th century development of the germ theory of infectious disease, have gone on to cause a continuing human problem. As it was, once the virologists had identified the virus and worked out its mechanism of spread, instituting rigorous sanitation procedures (especially hand washing) and practicing “barrier nursing” (latex gloves, face masks, disposable gowns) with afflicted patients led to the disease essentially “burning out” in humans. Authorities in the Middle East are, though, keeping a close watch on the closely related MERS coronavirus, which has caused a few human cases and may be maintained in nature as an asymptomatic infection of Egyptian tomb bats and camels. Could the MERS-CoV be the source of “The Curse of the Mummy’s Tomb”?
Even in the absence of specific antiviral drugs and vaccines, modern science protects us by defining the problem so that public health and medical professionals can take appropriate counter-measures. Still, though such viruses do not generally change their mode of transmission to spread readily by the dangerous respiratory route (we can’t choose when and where to breathe!), the basic message is that the price of freedom (from such infections) is constant vigilance. That’s why government agencies like the CDC and the US Public Health Service are so important for our defense. So far, the “worst-case” pandemic scenario for any hemorrhagic fever virus is that portrayed in the movie Contagion. Hopefully, a catastrophe of such magnitude will remain in the realm of fiction, but we do need to keep our guard up. The much more immediate and likely pandemic danger is always, so far as we are aware, from the influenza A viruses.
Peter C. Doherty is Chairman of the Department of Immunology at St. Jude’s Children’s Research Hospital, and a Laureate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Melbourne. He is the author of The Beginner’s Guide to Winning the Nobel Prize: Advice for Young Scientists, Their Fate is Our Fate: How Birds Foretell Threats to Our Health and Our World, published in Australia as Sentinel Chickens: What Birds Tell us About Our health and the World, A Light History of Hot Air and Pandemics: What Everyone Needs to Know.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only science and medicine articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image: Ebola virus virion. Public domain via Wikimedia Commons.
The post The Ebola virus and the spread of pandemics appeared first on OUPblog.

Contagion,” the extraordinary film portraying the outbreak of lethal virus that spreads rapidly around the world, may seem eerily familiar: from the medieval plague to the Spanish flu of 1918-19 to more recent fears of avian influenza, SARS, and H1N1 “swine flu”, contagions have long characterized the human condition. The film captures almost perfectly what a contemporary worst-case scenario might look like, and is eerily familiar because it trades on realistic fears. Contagion, the transmission of communicable infectious disease from one person to another (either by direct contact, as in this film — sneezing or coughing or touching one’s nose or mouth, then a surface like a tabletop or doorknob that someone else then touches





