Over the last few weeks, historian Gordon Martel, author of The Month That Changed The World: July 1914, has been blogging regularly for us, giving a week-by-week and day-by-day account of the events leading up to the First World War. July 1914 was the month that changed the world, but who were the people that contributed to that change? We wrap up the series with a Who’s Who of World War I below. Key countries have been highlighted with the corresponding figures and leaders that contributed to the outbreak of war.
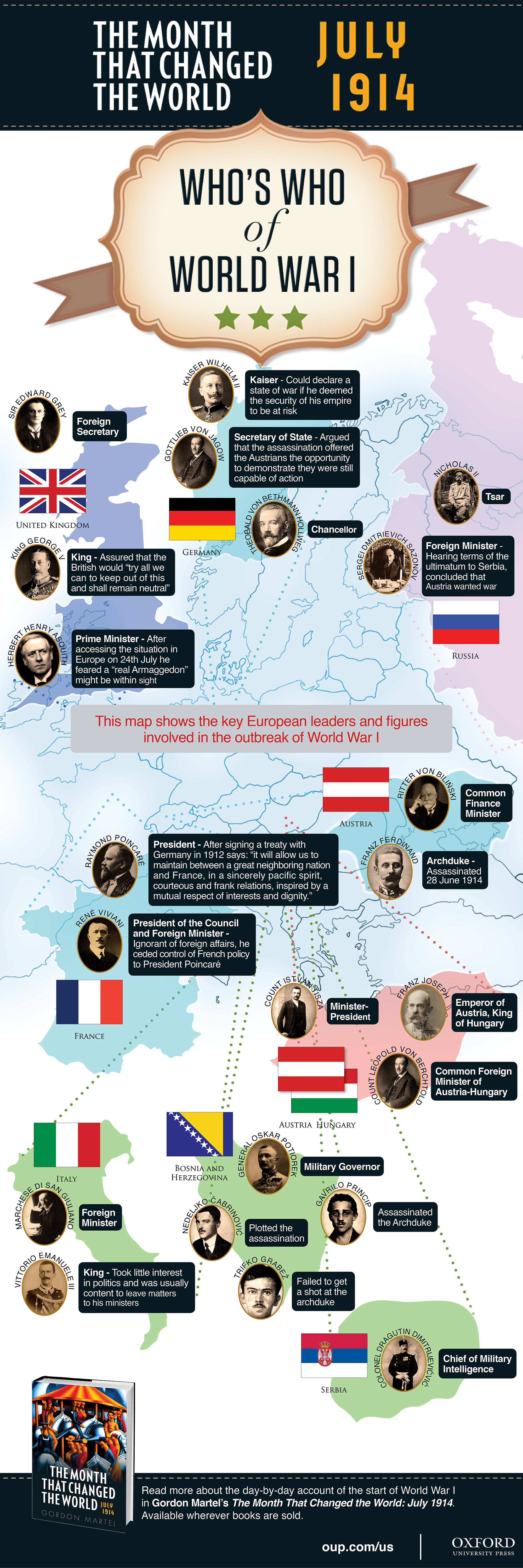
Download a jpeg or PDF of the map.
Gordon Martel is a leading authority on war, empire, and diplomacy in the modern age. His numerous publications include studies of the origins of the first and second world wars, modern imperialism, and the nature of diplomacy. A founding editor of The International History Review, he has taught at a number of Canadian universities, and has been a visiting professor or fellow in England, Ireland and Australia. Editor-in-chief of the five-volume Encyclopedia of War, he is also joint editor of the longstanding Seminar Studies in History series. His new book is The Month That Changed The World: July 1914.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only history articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post Political map of Who’s Who in World War I [infographic] appeared first on OUPblog.

July 1914 was the month that changed the world. On 28 June 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated, and just five weeks later the Great Powers of Europe were at war. But how did it all happen? Historian Gordon Martel, author of The Month That Changed The World: July 1914, is blogging regularly for us over the next few weeks, giving us a week-by-week and day-by-day account of the events that led up to the First World War.
By Gordon Martel
At 10 a.m. that morning the royal party arrived at the railway station. A motorcade consisting of six automobiles was to proceed from there along the Appel Quay to the city hall.The first automobile was to be manned by four special security detectives assigned to guard the archduke, but only one of them managed to take his place; local policemen substituted for the others. The next car was to carry the mayor, Fehim Effendi Čurćić, wearing his red fez, and the chief of police, Dr Edmund Gerde – who had warned the military authorities about the dangerous atmosphere in Sarajevo and had advised against proceeding with the visit.
The archduke and the duchess were seated next to one another in the third car, facing General Potiorek (the military governor of Bosnia) and the owner of the limousine, Count Harrach. The archduke and duchess conducted a brief inspection of the military barracks before setting out for the city hall, where they were to be formally welcomed before proceeding to open the new state museum, designed to display the benefits of Austrian rule.
Seven would-be assassins mingled with the gathering crowds for over an hour before the motorcade arrived. Ilić had assigned one of them, Nedeljko Čabrinović, a place across the street from two others stationed in front of the garden at the Mostar Café, situated near the first bridge on the route, the Čumurja. Ilić and another assassin took their places on the other side of the street; Gavrilo Princip was placed 200 yards further along the route, at the Lateiner bridge. All seven were in place when the royal party arrived at the station that morning.

The arrest of Gavrilo Princip
Ten minutes before the motorcade reached the Čumurja bridge a policeman approached Čabrinović, demanding that he identify himself. He produced a permit that purported to have been issued by the Viennese police and asked the policeman which car was carrying the archduke. ‘The third’ he was told. A few minutes later he took out his grenade, knocked off the detonator cap and threw it at the limousine carrying the archduke and the duchess. Because there was a twelve-second delay between knocking off the cap and the explosion, the grenade hit the limousine, bounced off, rolled under the next car, and exploded. General Potiorek’s aide-de-camp was injured, along with several spectators. The duchess suffered a slight wound to her cheek, where she had been grazed by the grenade’s detonator.
Čabrinović swallowed his cyanide capsule and jumped over the embankment into the river. But the cyanide failed and the river had been reduced to a mere trickle in mid-summer. He was captured immediately by a policeman who asked him if he was a Serb. ‘Yes, I am a Serb hero’, he replied.
The procession continued on its way to the splendid new city hall, the neo-Moorish Vijećnica, meant to evoke the Alhambra as part of Austria’s ‘neo-Orientalist’ policy designed to cultivate the support of Bosnia’s Muslims. When the royal party arrived, the mayor began to read the effusive speech he had prepared in their honour – apparently unaware of the near calamity that had just occurred. The archduke interrupted, angrily demanding to know how the mayor could speak of ‘loyalty’ to the crown when a bomb had just been thrown at him. The duchess, playing her accustomed role, managed to calm him down while they waited for a staff officer to arrive with a copy of the archduke’s speech – which was now splattered in blood.
After the speeches and a reception General Potiorek proposed that they either drive back along the Appel Quay at full speed to the station or go straight to his residence, only a few hundred metres away, and where lunch awaited them. But the archduke insisted on first visiting the wounded officer at the military hospital. The duchess insisted on accompanying him: ‘It is in time of danger that you need me.’
The royal couple, along with Potiorek, climbed into a new car, with Count Harrach standing on the footboard to shield the archduke from any other would-be assassins. A first car, with the chief of police and others, was to precede them. In order to reach the hospital the motorcade was forced to retrace its route along the Appel Quay. Princip, who had almost abandoned hopeafter Čabrinović’s arrest, was still waiting near the Lateiner bridge when the two cars unexpectedly appeared in front of him.
The driver of the first car had turned right off the Appel Quay, following the original route to take them to the museum; the driver of the second car followed him. General Potiorek, immediately recognizing the mistake, ordered his driver to stop. The car then began to reverse slowly in order to get back onto the Appel Quay – with Count Harrach now on the opposite side of the car to Princip, who was standing at the corner of Appel Quay and Franz Joseph Street, in front of Schiller’s delicatessen. Seizing the opportunity, Princip stepped out of the crowd. His moment had arrived.
Because it was too difficult to take the grenade out of his coat and knock off the detonator cap, Princip decided to use his revolver instead. A policeman spotted him and tried to intervene, but a friend of Princip’s kicked the policeman in the knee and knocked him off balance. The first shot hit the archduke near the jugular vein; the second hit the duchess in the stomach. ‘Soferl, Soferl!’ Franz Ferdinand cried, ‘Don’t die. Live for our children.’ The duchess was already dead by the time they reached the governor’s residence. The archduke, unconscious when he was carried inside, was also dead within minutes – before either a doctor or a priest could be summoned.
Spectators were attempting to lynch Princip when the police rescued him. He tried to swallow the cyanide capsule, but vomited it up. An Austrian judge, interviewing him almost immediately afterwards, wrote: ‘The young assassin, exhausted by his beating, was unable to utter a word. He was undersized, emaciated, sallow, sharp featured. It was difficult to imagine that so frail looking an individual could have committed so serious a deed.’
Gordon Martel is a leading authority on war, empire, and diplomacy in the modern age. His numerous publications include studies of the origins of the first and second world wars, modern imperialism, and the nature of diplomacy. A founding editor of The International History Review, he has taught at a number of Canadian universities, and has been a visiting professor or fellow in England, Ireland and Australia. Editor-in-chief of the five-volume Encyclopedia of War, he is also joint editor of the longstanding Seminar Studies in History series. His new book is The Month That Changed The World: July 1914.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only history articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Princip arrest [public domain]. Via Wikimedia Commons.
The post The month that changed the world: Sunday, 28 June 1914 appeared first on OUPblog.

July 1914 was the month that changed the world. On 28 June 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated, and just five weeks later the Great Powers of Europe were at war. But how did it all happen? Historian Gordon Martel, author of The Month That Changed The World: July 1914, will be blogging regularly for us over the next few weeks, giving us a week-by-week and day-by-day account of the events that led up to the First World War. His first post focuses on the events of Saturday, 27 June 1914.
By Gordon Martel
The next day was to be a brilliant one, a splendid occasion that would glorify the achievements of Austrian rule in Bosnia-Herzegovina. The Habsburg heir to the thrones of Austria and Hungary, the Archduke Franz Ferdinand, had been eagerly anticipating it for months. He envisioned making a triumphal entry into the city of Sarajevo, attired in his uniform as inspector-general of the Austro-Hungarian army, and accompanied by his wife, the duchess. Sophie would be resplendent in a full-length white dress with red sash tied at the waist, she would hold a parasol to shelter from the sun and a fan to cool her; gloves, furs and a magnificent hat would complete the outfit.
The date of Sunday, 28 June had been chosen carefully: it was the anniversary of the battle of Kosovo in 1389, at which the medieval Serbian kingdom had been extinguished by the victorious Turks. Afterwards, Bosnia and Herzegovina remained provinces of the Ottoman empire for almost 500 years, until occupied by Austro-Hungarian forces in 1878 and then annexed in 1908. Thus, on the occasion of the archduke’s visit, the Serbs of Bosnia were asked to pay homage to a member of the royal family that blocked the way to uniting all Serbs in a Greater Serbia. The location was also provocative: the archducal visit to Sarajevo was preceded by military manoeuvres in the mountains south of the city – not far from the frontier with Serbia.
The Austrians disregarded warnings of trouble. The Serbian minister in Vienna had suggested to the minister responsible for Bosnian affairs that some Serbs might regard the time and place of the visit as a deliberate affront. Perhaps, he warned, some young Serb participating in the Austrian manoeuvres might substitute live ammunition for blanks – and seize the opportunity to fire at the archduke. Politicians and officials on the spot in Sarajevo had advised that the visit be cancelled; the police warned that they could not guarantee the archduke’s safety, particularly given the lengthy route that that the royal couple were scheduled to take along the Miljačka river from the railway station to the city hall.

Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Franz Ferdinand was not to be dissuaded by any warnings. More than high politics was involved in the choice of date for the visit. 28 June was the 14th anniversary of the humiliating ‘oath of renunciation’ that Franz Ferdinand had been forced to swear in order to receive the approval of his uncle – the emperor— of his marriage to Sophie. According to Franz Joseph and Habsburg ‘house rules’, she was unsuitable: her family was merely aristocratic, and neither from the Habsburg family itself nor from one of the ruling dynasties of Europe. When the emperor, after a long and acrimonious battle with his nephew, reluctantly agreed to the marriage he had imposed the humiliating conditions of a ‘morganatic’ marriage: neither Sophie nor her offspring would possess the titles and rights that would normally have come with marriage; neither she nor their children could succeed to the throne. Franz Ferdinand, surrounded by archdukes, archduchesses and court officials, had sworn on a bible to uphold the oath in the Secret Council Chamber at the Hofburg Palace in Vienna. The ritual humiliation of Sophie had begun: although she was elevated to the status of ‘princess’ (and later to duchess) she would never become royalty. Her place, literally and figuratively, was lower than that of the youngest archduchess: in royal processions her husband would come first, she last, walking alone, without an escort. She was not permitted to sit at the head table at state dinners, could not share the royal box when attending the theatre or the opera. These insults aggrieved the volatile and temperamental archduke who was devoted to his wife.
Franz Ferdinand’s triumphal visit to Sarajevo the next day – on the 14th anniversary of the humiliating oath of renunciation – offered him the opportunity of seeing that Sophie would finally be treated with the respect that she was due. As wife of the inspector-general she was to sit next to him in an open carriage during the journey through the city and take the place of honour next to him when he addressed the dignitaries at city hall. Informally, late Saturday afternoon – the day before the official, ceremonial visit – he and Sophie took a leisurely journey into Sarajevo, where they were warmly welcomed by those who recognized them. The royal couple remained blissfully unaware that they had almost come face-to-face with the young Serb who was planning to kill the archduke the next day.
When the archduke and duchess attended the military ball on Saturday evening that marked the end of manoeuvres, Sophie was able to assure everyone how pleased she was with their reception in town that afternoon. At the same time the 19-year-old Danilo Ilić was meeting with six would-be assassins at a Sarajevo café. While handing out guns and grenades, he warned the others that the police may have discovered their plot. But there was no question of calling it off: such an opportunity as this was unlikely to occur again.
Ilić outlined the plan: the assassins were to be placed at each of the three bridges crossing the river. Their best chance of success would come at these junctions, where a grenade could easily be lobbed into the car carrying the royal couple. After discussing their plan, several of the conspirators visited the grave of Bogdan Žerajić, a young Serb who had been martyred years earlier when he had attempted (unsuccessfully) to assassinate the emperor. Legend had it that his dying words were ‘I leave it to Serbdom to avenge me’.
It proved enormously helpful to the conspirators that the plans for the procession on Sunday had been published in the local newspaper, the Bosnische Post – in order to encourage as many spectators as possible to turn out. Earlier that week the Muslim mayor had issued a proclamation calling on the people of the city to demonstrate their affection for the Habsburg heir to the throne: people should decorate their homes, fly the imperial flag and display pictures of the emperor and his nephew. The day was to be a triumph for Austro-Hungarian rule in Bosnia.
Gordon Martel is a leading authority on war, empire, and diplomacy in the modern age. His numerous publications include studies of the origins of the first and second world wars, modern imperialism, and the nature of diplomacy. A founding editor of The International History Review, he has taught at a number of Canadian universities, and has been a visiting professor or fellow in England, Ireland and Australia. Editor-in-chief of the five-volume Encyclopedia of War, he is also joint editor of the longstanding Seminar Studies in History series. His new book is The Month That Changed The World: July 1914.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only history articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Franz Ferdinand. By Carl Pietzner [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
The post The month that changed the world: Saturday, 27 June 1914 appeared first on OUPblog.

In honor of the centennial of World War I, we’re remembering the momentous period of history that forever changed the world as we know it. July 1914 was the month that changed the world. On 28 June 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated, and just five weeks later the Great Powers of Europe were at war. But how did it all happen? Historian Gordon Martel, author of The Month That Changed The World: July 1914, will be blogging regularly for us over the next few weeks, giving us a week-by-week and day-by-day account of the events that led up to the First World War. Before we dive in, here’s a timeline that provides an expansive overview of the monumental dates to remember.

Download a jpeg or PDF of the timeline.
Gordon Martel is the author of The Month that Changed the World: July 1914. He is a leading authority on war, empire, and diplomacy in the modern age. His numerous publications include studies of the origins of the first and second world wars, modern imperialism, and the nature of diplomacy. A founding editor of The International History Review, he has taught at a number of Canadian universities, and has been a visiting professor or fellow in England, Ireland and Australia. Editor-in-Chief of the five-volume Encyclopedia of War, he is also Joint Editor of the longstanding Seminar Studies in History series.
Visit the US ‘World War I: Commemorating the Centennial’ page or UK ‘First World War Centenary’ page to discover specially commissioned contributions from our expert authors, free resources from our world-class products, book lists, and exclusive archival materials that provide depth, perspective and insight into the Great War.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only history articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
The post The month that changed the world: a timeline to war appeared first on OUPblog.







