By Qiliang Ding and Ya Hu
Hominins and their closest living relative, chimpanzees, diverged approximately 6.5 million years ago on African continent. Fossil evidence suggests hominins have migrated away from Africa at least twice since then. Crania of the first wave of migrants, such as Neanderthals in Europe and Peking Man in East Asia, show distinct morphological features that are different from contemporary humans (also known as Homo sapiens sapiens). The first wave of migration was estimated to have occurred 7-9,000,000 years ago. In the 1990s, studies on Y-chromosome and mitochondrial DNA proved that the contemporary Eurasians are descendants of the second wave of migrants, who migrated out of Africa less than 100,000 years ago.
It has been reported that the habitats of Neanderthals and ancestors of contemporary Eurasians overlapped both in time and space, and therefore provides possibility of introgression between Neanderthals and ancestors of Eurasians. This possibility is confirmed by recent studies, which suggest that about 1-4% of Eurasian genomes are from Neanderthal introgression.
Adaptation to local environment is crucial for newly-arrived migrants, and the process of local adaptation is sometimes time-consuming. Since Neanderthals arrived in Eurasia ten times earlier than ancestors of Eurasians, we are trying to figure out whether the Neanderthal introgressions helped the ancestors of Eurasians adapt to the local environment.
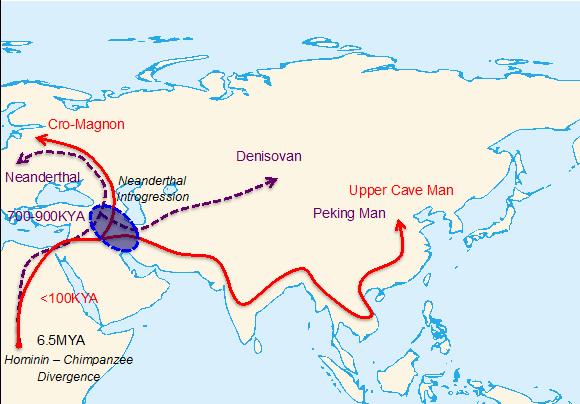
Two major out-of-Africa migration waves of hominins. The purple and red colors represent the first and second migration waves, respectively. The circle near Middle East represents a possible location where main Neanderthal introgression might have occurred.
Our study reports that Neanderthal introgressive segments on chromosome 3 may have helped East Asians adapting to the intensity of ultraviolet-B (UV-B) irradiation in sunlight. We call the region containing the Neanderthal introgression the “HYAL” region, as it contains three genes that encode hyaluronoglucosaminidases.
We first noticed that the entire HYAL region is included in an unusually large linkage disequilibrium (LD) block in East Asian populations. Such a large LD block is a typical signature of positive natural selection. More interestingly, it is observed that some Eurasian haplotypes at the HYAL region show a closer relationship to the Neanderthal haplotype than to the contemporary African haplotypes, implicating recent Neanderthal introgression. We confirmed the Neanderthal introgression in HYAL region by employing a series of statistical and population genetic analyses.
Further, we examined whether the HYAL region was under positive natural selection using two published statistical tests. Both suggest that the HYAL region was under positive natural selection, and pinpoint a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) contributed by Neanderthal introgression as the candidate targets of positive natural selection.
We then explored the potential functional importance of Neanderthal introgression in the HYAL region. The HYAL genes attracted our attention, as they are important in hyaluronan metabolism and cellular response to UV-B irradiation. We noticed that an SNP pinpointed as a potential target for positive natural selection was located in the most conservative exon of HYAL2 gene. We suspect that this SNP (known as rs35455589) may have altered the function of HYAL2 protein, since this SNP is also associated with the risk of keloid, a dermatological disorder related to hyaluronan metabolism.
Next, we interrogated the global distribution of Neanderthal introgression at the HYAL region. It is observed that the Neanderthal introgression reaches a very high frequency in East Asian populations, which ranges from 49.4% in Japanese to 66.5% in Southern Han Chinese. The frequency of Neanderthal introgression is higher in southern East Asian populations compared to northern East Asian populations. Such evidence might suggest latitude-dependent selection, which implicates the role of UV-B intensity.
We discovered that Neanderthal introgression on chromosome 3 was under positive natural selection in East Asians. We also found that a gene (HYAL2) in the introgressive region is related to the cellular response to UV-B, and an allele from Neanderthal introgression may have altered the function of HYAL2. As such, we think it is possible that Neanderthals may have helped East Asians to adapt to sunlight.
Qiliang Ding and Ya Hu are MSc Students at the Institute of Genetics at Fudan University and Intern Students at the CAS-MPG Partner Institute of Computational Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Their research interest lies in revealing evolutionary history of hominids using ancient and contemporary human genomes. They are the authors of the paper “Neanderthal Introgression at Chromosome 3p21.31 Was Under Positive Natural Selection in East Asians,” which appears in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Molecular Biology and Evolution publishes research at the interface of molecular (including genomics) and evolutionary biology.
Subscribe to the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Subscribe to only earth, environmental, and life sciences articles on the OUPblog via email or RSS.
Image credit: Background map via Wikimedia Commons, with annotations by the authors.
The post Neanderthals may have helped East Asians adapting to sunlight appeared first on OUPblog.


