Media coverage of health news can seem to consist of a steady diet of research-based stories, but making sense of what may be relevant or important and what is not can be a tall order for most patients. Headlines may shout about dramatic breakthroughs, exciting new advances, revolutions, and even cures but there may be scant details of the evidence base of the research.
The post How fertility patients can make informed decisions on treatment appeared first on OUPblog.
Does preconception stress increase the risk of infertility? Dr Courtney D. Lynch will be presenting the results from a couple-based prospective cohort study, the LIFE study, at this year’s Human Reproduction Keynote Lecture in Lisbon. We meet Dr Lynch to learn more about how she came to specialise in reproductive medicine and the findings of her research.
The post Preconception stress and infertility: a Q&A with Dr. Courtney D. Lynch appeared first on OUPblog.
A new study shows that women who have difficulty accepting the fact that they can’t have children following unsuccessful fertility treatment, have worse long-term mental health than women who are able to let go of their desire for children. It is the first to look at a large group of women (over 7,000) to try to disentangle the different factors that may affect women’s mental health over a decade after unsuccessful fertility treatment. These factors include whether or not they have children, whether they still want children, their diagnosis, and their medical treatment.
It was already known that people who have infertility treatment and remain childless have worse mental health than those who do manage to conceive with treatment. However, most previous research assumed that this was due exclusively to having children or not, and did not consider the role of other factors. Alongside my research colleagues from the Netherlands, where the study took place, we found only that there is a link between an unfulfilled wish for children and worse mental health, and not that the unfulfilled wish is causing the mental health problems. This is due to the nature of the study, in which the women’s mental health was measured at only one point in time rather than continuously since the end of fertility treatment.
We analysed answers to questionnaires completed by 7,148 women who started fertility treatment at any of 12 IVF hospitals in the Netherlands between 1995-2000. The questionnaires were sent out to the women between January 2011 and 2012, meaning that for most women their last fertility treatment would have been between 11-17 years ago. The women were asked about their age, marital status, education and menopausal status, whether the infertility was due to them, their partner, both or of unknown cause, and what treatment they had received, including ovarian stimulation, intrauterine insemination, and in vitro fertilisation / intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI). In addition, they completed a mental health questionnaire, which asked them how they felt during the past four weeks. The women were asked whether or not they had children, and, if they did, whether they were their biological children or adopted (or both). They were also asked whether they still wished for children.
The majority of women in the study had come to terms with the failure of their fertility treatment. However, 6% (419) still wanted children at the time of answering the study’s questionnaire and this was connected with worse mental health. We found that women who still wished to have children were up to 2.8 times more likely to develop clinically significant mental health problems than women who did not sustain a child-wish. The strength of this association varied according to whether women had children or not. For women with no children, those with a child-wish were 2.8 times more likely to have worse mental health than women without a child-wish. For women with children, those who sustained a child-wish were 1.5 times more likely to have worse mental health than those without a child-wish. This link between a sustained wish for children and worse mental health was irrespective of the women’s fertility diagnosis and treatment history.
Our research found that women had better mental health if the infertility was due to male factors or had an unknown cause. Women who started fertility treatment at an older age had better mental health than women who started younger, and those who were married or cohabiting with their partner reported better mental health than women who were single, divorced, or widowed. Better educated women also had better mental health than the less well educated.
This study improves our understanding of why childless people have poorer adjustment. It shows that it is more strongly associated with their inability to let go of their desire to have children. It is quite striking to see that women who do have children but still wish for more children report poorer mental health than those who have no children but have come to accept it. The findings underline the importance of psychological care of infertility patients and, in particular, more attention should be paid to their long-term adjustment, whatever the outcome of the fertility treatment.
The possibility of treatment failure should not be avoided during treatment and a consultation at the end of treatment should always happen, whether the treatment is successful or unsuccessful, to discuss future implications. This would enable fertility staff to identify patients more likely to have difficulties adjusting to the long term, by assessing the women’s possibilities to come to terms with their unfulfilled child-wish. These patients could be advised to seek additional support from mental health professionals and patient support networks.
It is not known why some women may find it more difficult to let go of their child-wish than others. Psychological theories would claim that how important the goal is for the person would be a relevant factor. The availability of other meaningful life goals is another relevant factor. It is easier to let go of a child-wish if women find other things in life that are fulfilling, like a career.
We live in societies that embrace determination and persistence. However, there is a moment when letting go of unachievable goals (be it parenthood or other important life goals) is a necessary and adaptive process for well-being. We need to consider if societies nowadays actually allow people to let go of their goals and provide them with the necessary mechanisms to realistically assess when is the right moment to let go.
Featured image: Baby feet by Nina-81. Public Domain via Pixabay.
The post Do children make you happier? appeared first on OUPblog.

By Dr Sesh Kamal Sunkara
In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves the retrieval of an egg and fertilization with sperm in the laboratory (in vitro) as opposed to the process happening within the human body (in vivo), with a natural conception. IVF was first introduced to overcome tubal factor infertility but has since been used to alleviate all types of infertility and nearly four million babies have been born worldwide as a result of assisted reproductive technology.
The birth of Louise Brown in 1978, the world’s first IVF baby was from a natural menstrual cycle without the use of any stimulation drugs. As success rates were low with natural cycles in the early days of IVF, ovarian stimulation regimens were introduced into IVF to maximize success rates. The aim was to retrieve more eggs to overcome the attrition in numbers at fertilization, cleavage, and implantation. However, with the introduction of ovarian stimulation regimens the complication of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) arose.
There have been several discussions among IVF clinicians on what the ideal number of eggs should be to optimize IVF outcome and minimize risk of OHSS. We analysed a large database of over 400, 000 cycles provided by the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) in order to establish the association between egg number and live birth rate in IVF.
We found that live birth rate increased with increasing number of eggs retrieved up to 15 eggs and plateaued from 15 to 20 eggs with a decline in live birth rate beyond 20. The analysis of the data suggested that around 15 eggs may be the optimal number to aim for in a fresh IVF cycle in order to maximize treatment success whilst minimizing the risk of OHSS. We also established a nomogram which is the first of its kind that allows prediction of live birth for a given egg number and female age group. This is potentially valuable for patients and clinicians in planning IVF treatment protocols and counselling regarding the prognosis for a live birth occurrence, especially in women with either predicted or a previous poor ovarian response.
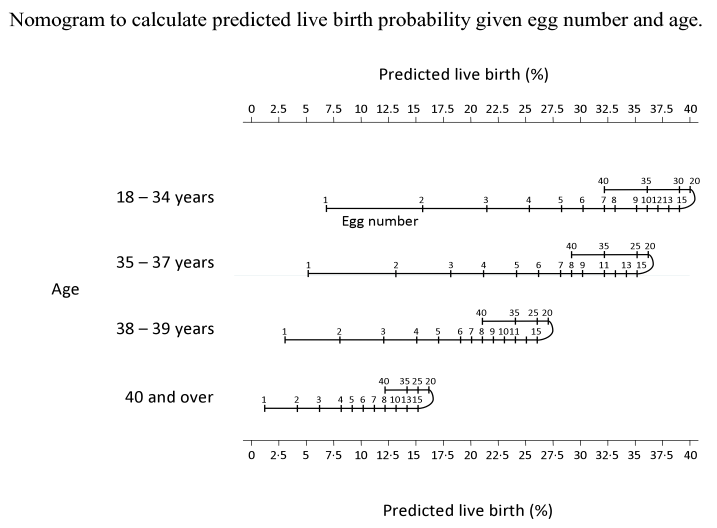
The full paper and supplementary data has been made publicly available here, as published in Human Reproduction by Sesh Kamal Sunkara, Vivian Rittenberg, Nick Raine-Fenning, Siladitya Bhattacharya, Javier Zamora and Arri Coomarasamy. Above table appears with full permission from Human Reproduction and Oxford Journals.





